Ferulic Acid Induces Keratin 6α via Inhibition of Nuclear β-Catenin Accumulation and Activation of Nrf2 in Wound-Induced Inflammation
- PMID: 33922346
- PMCID: PMC8146113
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9050459
Ferulic Acid Induces Keratin 6α via Inhibition of Nuclear β-Catenin Accumulation and Activation of Nrf2 in Wound-Induced Inflammation
Abstract
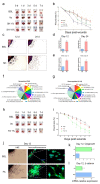
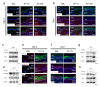
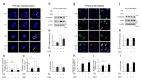
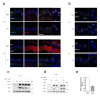
Injured tissue triggers complex interactions through biological process associated with keratins. Rapid recovery is most important for protection against secondary infection and inflammatory pain. For rapid wound healing with minimal pain and side effects, shilajit has been used as an ayurvedic medicine. However, the mechanisms of rapid wound closure are unknown. Here, we found that shilajit induced wound closure in an acute wound model and induced migration in skin explant cultures through evaluation of transcriptomics via microarray testing. In addition, ferulic acid (FA), as a bioactive compound, induced migration via modulation of keratin 6α (K6α) and inhibition of β-catenin in primary keratinocytes of skin explant culture and injured full-thickness skin, because accumulation of β-catenin into the nucleus acts as a negative regulator and disturbs migration in human epidermal keratinocytes. Furthermore, FA alleviated wound-induced inflammation via activation of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) at the wound edge. These findings show that FA is a novel therapeutic agent for wound healing that acts via inhibition of β-catenin in keratinocytes and by activation of Nrf2 in wound-induced inflammation.
Keywords: K6α; Nrf2; ferulic acid; keratinocytes; shilajit; wound healing; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lucidone Promotes the Cutaneous Wound Healing Process via Activation of the PI3K/AKT, Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017 Jan;1864(1):151-168. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.10.021. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 27816443
-
Gadd45a regulates matrix metalloproteinases by suppressing DeltaNp63alpha and beta-catenin via p38 MAP kinase and APC complex activation.Oncogene. 2004 Mar 11;23(10):1829-37. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207301. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 14647429
-
In vitro wound healing activity of 1-hydroxy-5,7-dimethoxy-2-naphthalene-carboxaldehyde (HDNC) and other isolates of Aegle marmelos L.: Enhances keratinocytes motility via Wnt/β-catenin and RAS-ERK pathways.Saudi Pharm J. 2019 May;27(4):532-539. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.01.017. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Saudi Pharm J. 2019. PMID: 31061622 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and calcium regulation of epidermal wound healing.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Nov;164:379-385. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 14. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26282157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Role of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Wound Healing Process.Molecules. 2021 Apr 21;26(9):2424. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092424. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33919399 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ferulic Acid: A Review of Mechanisms of Action, Absorption, Toxicology, Application on Wound Healing.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2024;23(4):205-214. doi: 10.2174/0118715230309592240723105514. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39108119 Review.
-
Intermediate filaments and their associated molecules.J Biomed Res. 2025 Feb 8;39(3):242-253. doi: 10.7555/JBR.38.20240193. J Biomed Res. 2025. PMID: 39930669 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Herbal-Derived Products with Skin Anti-Aging Properties and Cosmetic Applications.Molecules. 2022 Nov 3;27(21):7518. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217518. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Discovery of Novel Drugs on Natural Molecules.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 5;12(6):1254. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061254. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927461 Free PMC article.
-
Shilajit potentiates the effect of chemotherapeutic drugs and mitigates metastasis induced liver and kidney damages in osteosarcoma rats.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Sep;29(9):103393. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103393. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35957703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Demidova-Rice T.N., Hamblin M.R., Herman I.M. Acute and Impaired Wound Healing: Pathophysiology and current methods for drug delivery, part 1: Normal and chronic wounds: Biology, causes, and approaches to care. Adv. Ski. Wound Care. 2012;25:304–314. doi: 10.1097/01.ASW.0000416006.55218.d0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Paladini R.D., Takahashi K., Bravo N.S., Coulombe P. Onset of re-epithelialization after skin injury correlates with a reorganization of keratin filaments in wound edge keratinocytes: Defining a potential role for keratin 16. J. Cell Biol. 1996;132:381–397. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.3.381. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

