Small GTPases of the Rab and Arf Families: Key Regulators of Intracellular Trafficking in Neurodegeneration
- PMID: 33922618
- PMCID: PMC8122874
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094425
Small GTPases of the Rab and Arf Families: Key Regulators of Intracellular Trafficking in Neurodegeneration
Abstract
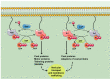
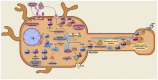
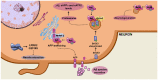
Small guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases) of the Rab and Arf families are key regulators of vesicle formation and membrane trafficking. Membrane transport plays an important role in the central nervous system. In this regard, neurons require a constant flow of membranes for the correct distribution of receptors, for the precise composition of proteins and organelles in dendrites and axons, for the continuous exocytosis/endocytosis of synaptic vesicles and for the elimination of dysfunctional proteins. Thus, it is not surprising that Rab and Arf GTPases have been associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Both pathologies share characteristics such as the presence of protein aggregates and/or the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus, hallmarks that have been related to both Rab and Arf GTPases functions. Despite their relationship with neurodegenerative disorders, very few studies have focused on the role of these GTPases in the pathogenesis of neurodegeneration. In this review, we summarize their importance in the onset and progression of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, as well as their emergence as potential therapeutical targets for neurodegeneration.
Keywords: Alzheimer; Arf GTPase; Parkinson; Rab GTPase; membrane trafficking; neurodegeneration; small GTPase; transport; vesicle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. All authors qualify for authorship, approved the final version of the manuscript, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the research in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the study are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Figures
References
-
- Goitre L., Trapani E., Trabalzini L., Retta S.F. The Ras Superfamily of Small GTPases: The Unlocked Secrets. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014;1120:1–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PRE_2017_1_0016/A.A.S. is a recipient of a predoctoral fellowship (PRE_2017_1_0016) from the Basque Government.
- Foundation "Jesús de Gangoiti y Barrera"/M.L.M. is a recipient of a fellowship from Foundation "Jesús de Gangoiti y Barrera".
- PI18/00207/J.L.Z. was supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- US19/04/J.L.Z. was supported by the University of Basque Country Grant
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

