Association of Urinary and Plasma Levels of Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) with Foods
- PMID: 33922680
- PMCID: PMC8145508
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13051426
Association of Urinary and Plasma Levels of Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) with Foods
Abstract
Introduction: Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) may play a key mediator role in the relationship between the diet, gut microbiota and cardiovascular diseases, particularly in people with kidney failure. The aim of this review is to evaluate which foods have a greater influence on blood or urinary trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) levels.
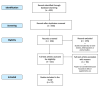
Methods: 391 language articles were screened, and 27 were analysed and summarized for this review, using the keywords "TMAO" AND "egg" OR "meat" OR "fish" OR "dairy" OR "vegetables" OR "fruit" OR "food" in December 2020.
Results: A strong correlation between TMAO and fish consumption, mainly saltwater fish and shellfish, but not freshwater fish, has been demonstrated. Associations of the consumption of eggs, dairy and meat with TMAO are less clear and may depend on other factors such as microbiota or cooking methods. Plant-based foods do not seem to influence TMAO but have been less investigated.
Discussion: Consumption of saltwater fish, dark meat fish and shellfish seems to be associated with an increase in urine or plasma TMAO values. Further studies are needed to understand the relationship between increased risk of cardiovascular disease and plasma levels of TMAO due to fish consumption. Interventions coupled with long-term dietary patterns targeting the gut microbiota seem promising.
Keywords: TMAO; dairy; eggs; fish; foods; meat; microbiota; trimethylamine N-oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Influence of Animal- or Plant-Based Diets on Blood and Urine Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO) Levels in Humans.Curr Nutr Rep. 2022 Mar;11(1):56-68. doi: 10.1007/s13668-021-00387-9. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Curr Nutr Rep. 2022. PMID: 34990005 Review.
-
Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) response to animal source foods varies among healthy young men and is influenced by their gut microbiota composition: A randomized controlled trial.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017 Jan;61(1). doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201600324. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017. PMID: 27377678 Clinical Trial.
-
Associations of current diet with plasma and urine TMAO in the KarMeN study: direct and indirect contributions.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017 Nov;61(11). doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201700363. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017. PMID: 28755411
-
Trimethylamine N-Oxide Plasma Levels Following Red Meat and Cod Fish Intake: A Pilot Crossover Trial in Hemodialysis Patients.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2025 Apr;69(8):e70031. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.70031. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2025. PMID: 40079058
-
Dietary bioactive ingredients to modulate the gut microbiota-derived metabolite TMAO. New opportunities for functional food development.Food Funct. 2020 Aug 1;11(8):6745-6776. doi: 10.1039/d0fo01237h. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Food Funct. 2020. PMID: 32686802 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota-derived trimethylamine N-Oxide: a novel target for the treatment of preeclampsia.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2311888. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2311888. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 38351748 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Animal- or Plant-Based Diets on Blood and Urine Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO) Levels in Humans.Curr Nutr Rep. 2022 Mar;11(1):56-68. doi: 10.1007/s13668-021-00387-9. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Curr Nutr Rep. 2022. PMID: 34990005 Review.
-
The Effect of Red Meat Consumption on Circulating, Urinary, and Fecal Trimethylamine-N-Oxide: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Adv Nutr. 2025 Jul;16(7):100453. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2025.100453. Epub 2025 May 24. Adv Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40419218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of TMAO on the incidence and prognosis of cerebral infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1287928. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1287928. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38259655 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Diet with Urinary Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO) and Its Precursors among Free-Living 10-Year-Old Children: Data from SMBCS.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 19;14(16):3419. doi: 10.3390/nu14163419. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36014922 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources