Can Alveolar-Arterial Difference and Lung Ultrasound Help the Clinical Decision Making in Patients with COVID-19?
- PMID: 33922829
- PMCID: PMC8145474
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11050761
Can Alveolar-Arterial Difference and Lung Ultrasound Help the Clinical Decision Making in Patients with COVID-19?
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 is an emerging infectious disease, that is heavily challenging health systems worldwide. Admission Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) and Lung Ultrasound (LUS) can be of great help in clinical decision making, especially during the current pandemic and the consequent overcrowding of the Emergency Department (ED). The aim of the study was to demonstrate the capability of alveolar-to-arterial oxygen difference (AaDO2) in predicting the need for subsequent oxygen support and survival in patients with COVID-19 infection, especially in the presence of baseline normal PaO2/FiO2 ratio (P/F) values.
Methods: A cohort of 223 swab-confirmed COVID-19 patients underwent clinical evaluation, blood tests, ABG and LUS in the ED. LUS score was derived from 12 ultrasound lung windows. AaDO2 was derived as AaDO2 = ((FiO2) (Atmospheric pressure - H2O pressure) - (PaCO2/R)) - PaO2. Endpoints were subsequent oxygen support need and survival.
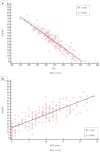
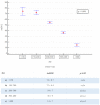
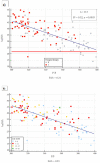
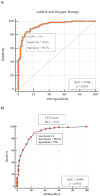
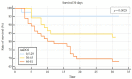
Results: A close relationship between AaDO2 and P/F and between AaDO2 and LUS score was observed (R2 = 0.88 and R2 = 0.67, respectively; p < 0.001 for both). In the subgroup of patients with P/F between 300 and 400, 94.7% (n = 107) had high AaDO2 values, and 51.4% (n = 55) received oxygen support, with 2 ICU admissions and 10 deaths. According to ROC analysis, AaDO2 > 39.4 had 83.6% sensitivity and 90.5% specificity (AUC 0.936; p < 0.001) in predicting subsequent oxygen support, whereas a LUS score > 6 showed 89.7% sensitivity and 75.0% specificity (AUC 0.896; p < 0.001). Kaplan-Meier curves showed different mortality in the AaDO2 subgroups (p = 0.0025).
Conclusions: LUS and AaDO2 are easy and effective tools, which allow bedside risk stratification in patients with COVID-19, especially when P/F values, signs, and symptoms are not indicative of severe lung dysfunction.
Keywords: COVID-19; P/F; arterial-alveolar difference; emergency department; lung injury; lung ultrasound; pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lung Ultrasound Score in COVID-19 Patients Correlates with PO2/FiO2, Intubation Rates, and Mortality.West J Emerg Med. 2024 Jan;25(1):28-39. doi: 10.5811/westjem.59975. West J Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 38205982 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of Intensive Care Unit admission in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2020 Jul 15;90(3). doi: 10.4081/monaldi.2020.1410. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2020. PMID: 32672430
-
Role of Lung Ultrasound in the Management of Patients with Suspected SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Emergency Department.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 7;11(8):2067. doi: 10.3390/jcm11082067. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35456160 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial blood gas analysis utility in predicting lung injury in blunt chest trauma.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2020 Mar;274:103363. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2019.103363. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31866500
-
Exercise induced arterial hypoxemia: the role of ventilation-perfusion inequality and pulmonary diffusion limitation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;588:17-30. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-34817-9_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 17089876 Review.
Cited by
-
Alveolar Arterial Gradient and Respiratory Index in Predicting the Outcome of COVID-19 Patients; a Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study.Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2022 Apr 14;10(1):e28. doi: 10.22037/aaem.v10i1.1543. eCollection 2022. Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2022. PMID: 35573712 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenic pulmonary edema and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2023 Dec;165(12):3677-3684. doi: 10.1007/s00701-023-05824-y. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2023. PMID: 37924360
-
Comparison of positive pressure extubation with traditional extubation in critically ill patients - a randomised control study.Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2023;55(1):38-45. doi: 10.5114/ait.2023.125584. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2023. PMID: 37306270 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lung Ultrasound Score in COVID-19 Patients Correlates with PO2/FiO2, Intubation Rates, and Mortality.West J Emerg Med. 2024 Jan;25(1):28-39. doi: 10.5811/westjem.59975. West J Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 38205982 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Ultrasound: A Diagnostic Leading Tool for SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia: A Narrative Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Dec 17;11(12):2381. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11122381. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943618 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. [(accessed on 11 March 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-a....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

