MiR-182-5p and miR-375-3p Have Higher Performance Than PSA in Discriminating Prostate Cancer from Benign Prostate Hyperplasia
- PMID: 33922968
- PMCID: PMC8123314
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13092068
MiR-182-5p and miR-375-3p Have Higher Performance Than PSA in Discriminating Prostate Cancer from Benign Prostate Hyperplasia
Abstract
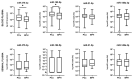
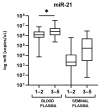
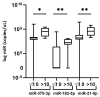
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most commonly diagnosed neoplasm among men. Since it often resembles benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH), biomarkers with a higher differential value than PSA are required. Epigenetic biomarkers in liquid biopsies, especially miRNA, could address this challenge. The absolute expression of miR-375-3p, miR-182-5p, miR-21-5p, and miR-148a-3p were quantified in blood plasma and seminal plasma of 65 PCa and 58 BPH patients by digital droplet PCR. The sensitivity and specificity of these microRNAs were determined using ROC curve analysis. The higher expression of miR-182-5p and miR-375-3p in the blood plasma of PCa patients was statistically significant as compared to BPH (p = 0.0363 and 0.0226, respectively). Their combination achieved a specificity of 90.2% for predicting positive or negative biopsy results, while PSA cut-off of 4 µg/L performed with only 1.7% specificity. In seminal plasma, miR-375-3p, miR-182-5p, and miR-21-5p showed a statistically significantly higher expression in PCa patients with PSA >10 µg/L compared to ones with PSA ≤10 µg/L. MiR-182-5p and miR-375-3p in blood plasma show higher performance than PSA in discriminating PCa from BPH. Seminal plasma requires further investigation as it represents an obvious source for PCa biomarker identification.
Keywords: benign prostate hyperplasia; biomarkers; liquid biopsy; microRNA; plasma; prostate cancer; seminal fluid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Global Cancer Observatory. [(accessed on 17 August 2020)]; Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

