Mediating Roles of Cognitive Complaints on Relationships between Insomnia, State Anxiety, and Presenteeism in Japanese Adult Workers
- PMID: 33923141
- PMCID: PMC8123047
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18094516
Mediating Roles of Cognitive Complaints on Relationships between Insomnia, State Anxiety, and Presenteeism in Japanese Adult Workers
Abstract
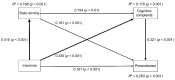
Complaints of cognitive functions (CCFs), defined as subjective cognitive dysfunction, affect social function; additionally, for workers, this condition is an important factor in presenteeism and mediates the effect of depressive symptoms on presenteeism. This study aimed to investigate whether CCFs mediate the relationships among insomnia, state anxiety (SA), and presenteeism. Participants were 471 Japanese adult workers evaluated using the Athens Insomnia Scale, State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (Form Y), Cognitive Complaints in Bipolar Disorder Rating Assessment, and Work Limitations Questionnaire 8 to assess insomnia, SA, CCFs, and presenteeism, respectively. Path analysis was used to evaluate the correlations between variables. CCFs significantly mediated the associations among insomnia, SA, and presenteeism. To address the presenteeism associated with insomnia and SA, it may be useful to assess the mediating roles of CCFs.
Keywords: cognitive complaints; insomnia; mediator; presenteeism; state anxiety.
Conflict of interest statement
J.M. has received personal compensation from Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly, Astellas, and Meiji Yasuda Mental Health Foundation, as well as grants from Pfizer. I.K. has received honoraria from Daiichi Sankyo, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Lundbeck, Meiji Seika Pharma, Mochida Pharmaceutical, Mylan, Novartis Pharma, Ono Pharmaceutical, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Shionogi, Shire, Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Tsumura, and Yoshitomiyakuhin, and has received research/grant support from Asahi Kasei Pharma, Astellas, Daiichi Sankyo, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Mochida Pharmaceutical, Novartis Pharma, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Shionogi, Takeda Pharmaceutical and Tanabe Mitsubishi Pharma. T.I. is a member of the advisory boards of Pfizer, Novartis Pharma, and Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma and has received personal fees from Mochida Pharmaceutical, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical, Yoshitomiyakuhin, and Daiichi Sankyo; he has received grants from Shionogi, Astellas, Tsumura, and Eisai and grants and personal fees from Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Kyowa Pharmaceutical Industry, Pfizer, Novartis Pharma, and Meiji Seika Pharma. Y.F. received research and grant support from Novartis Pharma, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Astellas, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, and Shionogi. S.H. has received honoraria from Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma and Novartis Pharma. A.S. reports personal fees from Eisai, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, MSD, Yoshitomi Yakuhin, and Meiji Seika Pharma, outside the submitted work. Y.U. has received lecture fees from Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma. K.T. does not have any actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations Between Cognitive Impairment, Depressive Symptoms, and Work Productivity Loss in Patients With Bipolar Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Analysis.Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2025 Mar;45(1):e70012. doi: 10.1002/npr2.70012. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40113345 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between the depressive symptoms, subjective cognitive function, and presenteeism of Japanese adult workers: a cross-sectional survey study.Biopsychosoc Med. 2020 May 4;14:10. doi: 10.1186/s13030-020-00183-x. eCollection 2020. Biopsychosoc Med. 2020. PMID: 32391075 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive complaints mediate the influence of sleep disturbance and state anxiety on subjective well-being and ill-being in adult community volunteers: a cross sectional study.BMC Public Health. 2022 Mar 22;22(1):566. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-12936-0. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35317767 Free PMC article.
-
Association between insomnia severity and presenteeism among Japanese daytime workers.J Sleep Res. 2023 Feb;32(1):e13711. doi: 10.1111/jsr.13711. Epub 2022 Aug 25. J Sleep Res. 2023. PMID: 36054731
-
Subjective cognitive impairment and presenteeism mediate the associations of rumination with subjective well-being and ill-being in Japanese adult workers from the community.Biopsychosoc Med. 2021 Oct 2;15(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13030-021-00218-x. Biopsychosoc Med. 2021. PMID: 34600577 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sleep Valuation Is Associated with Components of Sleep Health and Daytime Functioning in a College Sample: A Survey Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 25;18(11):5644. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18115644. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34070462 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of online exercise intervention on physical and mental conditions in young adults with chronic neck pain.iScience. 2023 Nov 23;26(12):108543. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108543. eCollection 2023 Dec 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38162023 Free PMC article.
-
Limited social support is associated with depression, anxiety, and insomnia in a Japanese working population.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 21;10:981592. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.981592. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36483246 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between presenteeism, quality of life and social support in higher education professionals: A cross-sectional path analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 21;17(4):e0267514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267514. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35446913 Free PMC article.
-
Victimization in Childhood Influences Presenteeism in Adulthood via Mediation by Neuroticism and Perceived Job Stressors.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022 Feb 15;18:265-274. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S343844. eCollection 2022. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022. PMID: 35210774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leka S., Griffiths A., Cox T., World Health Organization . Work Organisation & Stress: Systematic Problem Approaches for Employers, Managers and Trade Union Representatives. Institute of Work, Health & Organisations; Nottingham, UK: 2003. Protecting Workers Health Series: 3.
-
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development . Sick on the Job? Myths and Realities about Mental Health and Work. OECD Publishing; Paris, France: 2012.
-
- Spielberger C.D. Understanding Stress and Anxiety. Harper and Row; New York, NY, USA: 1979.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

