Theoretical Models of Consciousness: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 33923218
- PMCID: PMC8146510
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci11050535
Theoretical Models of Consciousness: A Scoping Review
Abstract
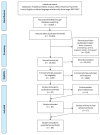
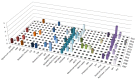
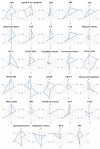
The amount of knowledge on human consciousness has created a multitude of viewpoints and it is difficult to compare and synthesize all the recent scientific perspectives. Indeed, there are many definitions of consciousness and multiple approaches to study the neural correlates of consciousness (NCC). Therefore, the main aim of this article is to collect data on the various theories of consciousness published between 2007-2017 and to synthesize them to provide a general overview of this topic. To describe each theory, we developed a thematic grid called the dimensional model, which qualitatively and quantitatively analyzes how each article, related to one specific theory, debates/analyzes a specific issue. Among the 1130 articles assessed, 85 full texts were included in the prefinal step. Finally, this scoping review analyzed 68 articles that described 29 theories of consciousness. We found heterogeneous perspectives in the theories analyzed. Those with the highest grade of variability are as follows: subjectivity, NCC, and the consciousness/cognitive function. Among sub-cortical structures, thalamus, basal ganglia, and the hippocampus were the most indicated, whereas the cingulate, prefrontal, and temporal areas were the most reported for cortical ones also including the thalamo-cortical system. Moreover, we found several definitions of consciousness and 21 new sub-classifications.
Keywords: cognition; consciousness; consciousness definition; consciousness theory; neural correlates; subjectivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sommerhoff G. Consciousness explained as an internal integrating system. J. Conscious. Stud. 1996;3:139–157.
-
- Monzavi M., Murad M.H.S.A., Rahnama M., Shamshirband S. Historical path of traditional and modern idea of ‘conscious universe’. Qual. Quant. 2016;51:1183–1195. doi: 10.1007/s11135-016-0324-3. - DOI
-
- Capra F. The Tao of Physics. Shambhala Publications; Boston, MA, USA: 1974.
-
- Clark A. Supersizing the Mind: Embodiment, Action, and Cognitive Extension. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2008.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

