Dopamine Transporter Genetic Reduction Induces Morpho-Functional Changes in the Enteric Nervous System
- PMID: 33923250
- PMCID: PMC8146213
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9050465
Dopamine Transporter Genetic Reduction Induces Morpho-Functional Changes in the Enteric Nervous System
Abstract
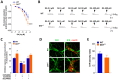
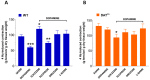
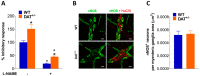
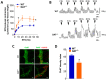
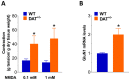
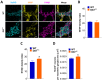
Antidopaminergic gastrointestinal prokinetics are indeed commonly used to treat gastrointestinal motility disorders, although the precise role of dopaminergic transmission in the gut is still unclear. Since dopamine transporter (DAT) is involved in several brain disorders by modulating extracellular dopamine in the central nervous system, this study evaluated the impact of DAT genetic reduction on the morpho-functional integrity of mouse small intestine enteric nervous system (ENS). In DAT heterozygous (DAT+/-) and wild-type (DAT+/+) mice (14 ± 2 weeks) alterations in small intestinal contractility were evaluated by isometrical assessment of neuromuscular responses to receptor and non-receptor-mediated stimuli. Changes in ENS integrity were studied by real-time PCR and confocal immunofluorescence microscopy in longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus whole-mount preparations (). DAT genetic reduction resulted in a significant increase in dopamine-mediated effects, primarily via D1 receptor activation, as well as in reduced cholinergic response, sustained by tachykininergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission via NMDA receptors. These functional anomalies were associated to architectural changes in the neurochemical coding and S100β immunoreactivity in small intestine myenteric plexus. Our study provides evidence that genetic-driven DAT defective activity determines anomalies in ENS architecture and neurochemical coding together with ileal dysmotility, highlighting the involvement of dopaminergic system in gut disorders, often associated to neurological conditions.
Keywords: confocal microscopy; dopamine transporter; enteric nervous system; neuromuscular contractility; small intestine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Small intestine neuromuscular dysfunction in a mouse model of dextran sulfate sodium-induced ileitis: Involvement of dopaminergic neurotransmission.Life Sci. 2022 Jul 15;301:120562. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120562. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35487304
-
Oxidized phospholipids affect small intestine neuromuscular transmission and serotonergic pathways in juvenile mice.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021 Apr;33(4):e14036. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14036. Epub 2020 Nov 22. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021. PMID: 33222337
-
Involvement of Enteric Glia in Small Intestine Neuromuscular Dysfunction of Toll-Like Receptor 4-Deficient Mice.Cells. 2020 Mar 31;9(4):838. doi: 10.3390/cells9040838. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32244316 Free PMC article.
-
The nature of catecholamine-containing neurons in the enteric nervous system in relationship with organogenesis, normal human anatomy and neurodegeneration.Arch Ital Biol. 2017 Sep 1;155(3):118-130. doi: 10.12871/00039829201733. Arch Ital Biol. 2017. PMID: 29220864 Review.
-
In vivo imaging of synaptic function in the central nervous system: II. Mental and affective disorders.Behav Brain Res. 2009 Dec 1;204(1):32-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2009.06.009. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Behav Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19523495 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Neuroendocrine signalling pathways along the microbiota-gut-brain axis in functional gut disorders.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 21;13:996382. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.996382. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36213279 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Influence of Tilia tomentosa Moench Extract on Mouse Small Intestine Neuromuscular Contractility.Nutrients. 2021 Oct 4;13(10):3505. doi: 10.3390/nu13103505. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34684506 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of wholemount dissection methods for neuronal subtype marker expression in the mouse myenteric plexus.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2024 Jan;36(1):e14693. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14693. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2024. PMID: 37882149 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal Dopamine in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 29;22(23):12932. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312932. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884737 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine in Health and Disease.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 9;9(11):1644. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111644. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829873 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

