Changes in Alcohol Consumption during the COVID-19 Pandemic-Small Change in Total Consumption, but Increase in Proportion of Heavy Drinkers
- PMID: 33923567
- PMCID: PMC8073387
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18084231
Changes in Alcohol Consumption during the COVID-19 Pandemic-Small Change in Total Consumption, but Increase in Proportion of Heavy Drinkers
Abstract
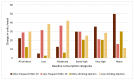
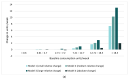
Little is known about possible changes in alcohol consumption distribution during the COVID-19 pandemic. We estimated how individual changes in alcohol consumption during the pandemic translated into changes in: (i) mean consumption; (ii) dispersion of consumption distribution; and (iii) prevalence of heavy drinkers. We employed data from two independent web-surveys of Norwegian adults collected between April and July 2020 and limited to those reporting past year alcohol consumption (N1 = 15,267, N2 = 1195). Self-reports of changes in drinking behavior were quantified, assuming change being relative to baseline consumption level. During the pandemic, we found a small increase (Survey 1) or no change (Survey 2) in estimated mean alcohol consumption (which parallels to total consumption). However, in both surveys, the dispersion of the distribution increased significantly (p < 0.001). For most respondents, an average modest decline in consumption was found. However, the small fraction with the highest baseline consumption increased their consumption substantially, and in effect, the proportion of heavy drinkers increased markedly (p < 0.001). In conclusion, quantifications of reported changes in alcohol consumption during the pandemic suggest that the upper 5 to 10% of the drinkers increased their consumption and hence the prevalence of heavy drinkers increased, despite little or no change in total alcohol consumption.
Keywords: COVID-19; Norway; alcohol use; changes; distribution of consumption; heavy drinkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shield K., Manthey J., Rylett M., Probst C., Wettlaufer A., Parry C.D.H., Rehm J. National, regional, and global burdens of disease from 2000 to 2016 attributable to alcohol use: A comparative risk assessment study. Lancet Public Health. 2020;5:e51–e61. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30231-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Griswold M.G., Fullman N., Hawley C., Arian N., Zimsen S.R.M., Tymeson H.D., Venkateswaran V., Tapp A.D., Forouzanfar M.H., Salama J.S., et al. Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2018;392:1015–1035. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31310-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

