Cannabinoid Receptor Type-2 in B Cells Is Associated with Tumor Immunity in Melanoma
- PMID: 33923757
- PMCID: PMC8073134
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13081934
Cannabinoid Receptor Type-2 in B Cells Is Associated with Tumor Immunity in Melanoma
Abstract
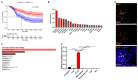
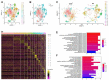
Agents targeting the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have gained attention as potential cancer treatments. Given recent evidence that cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2R) regulates lymphocyte development and inflammation, we performed studies on CB2R in the immune response against melanoma. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data revealed a strong positive correlation between CB2R expression and survival, as well as B cell infiltration in human melanoma. In a murine melanoma model, CB2R expression reduced the growth of melanoma as well as the B cell frequencies in the tumor microenvironment (TME), compared to CB2R-deficient mice. In depth analysis of tumor-infiltrating B cells using single-cell RNA sequencing suggested a less differentiated phenotype in tumors from Cb2r-/- mice. Thus, in this study, we demonstrate for the first time a protective, B cell-mediated role of CB2R in melanoma. This gained insight might assist in the development of novel, CB2R-targeted cancer therapies.
Keywords: CB2R; cannabinoid receptor type-2; endocannabinoid system; melanoma; regulatory B cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Muir R. Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;355:51–65. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

