Surgical Treatment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 33923884
- PMCID: PMC8074119
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13081971
Surgical Treatment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) represents an aggressive tumor of the digestive system with still low five-year survival of less than 10%. Although there are improvements for multimodal therapy of PDAC, surgery still remains the effective way to treat the disease. Combined with adjuvant and/or neoadjuvant treatment, pancreatic surgery is able to enhance the five-year survival up to around 20%. However, pancreatic resection is always associated with a high risk of complications and regarded as one of the most complex fields in abdominal surgery. This review gives a summary on the surgical treatment for PDAC based on the current literature with a special focus on resection techniques.
Keywords: pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; surgical treatment; technical advances.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

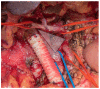
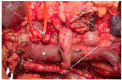
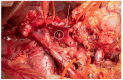
References
-
- Hackert T., Sachsenmaier M., Hinz U., Schneider L., Michalski C.W., Springfeld C., Strobel O., Jager D., Ulrich A., Buchler M.W. Locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Neoadjuvant therapy with folfirinox results in resectability in 60% of the patients. Ann. Surg. 2016;264:457–463. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001850. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Satoi S., Yamamoto T., Uchida K., Fujii T., Kin T., Hirano S., Hanada K., Itoi T., Murakami Y., Igarashi H., et al. Optimal treatment for octogenarians with resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A multicenter retrospective study. Pancreas. 2020;49:837–844. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001579. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

