Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis of Cervical Spine with Dysphagia-Molecular and Clinical Aspects
- PMID: 33923907
- PMCID: PMC8074005
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22084255
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis of Cervical Spine with Dysphagia-Molecular and Clinical Aspects
Abstract
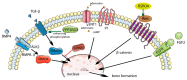
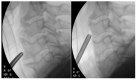
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is a condition characterized by the calcification and ossification of the ligaments of the cervical spine; in some cases, it may result in dysphagia. The condition is more common in men over 50 years of age with metabolic disorders, and it is often asymptomatic and not a major issue for patients. The etiology of DISH is poorly understood, and known genetic factors indicate multiple signal pathways and multigene inheritance. In this review, we discuss the epidemiological, clinical, and etiological aspects of DISH with a special focus on dysphagia.
Keywords: DISH; DISHphagia; Forestier disease; cervical spine; diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis; dysphagia; molecular and genetical factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

