Viral Infection Modulates Mitochondrial Function
- PMID: 33923929
- PMCID: PMC8073244
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22084260
Viral Infection Modulates Mitochondrial Function
Abstract
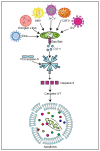
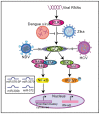
Mitochondria are important organelles involved in metabolism and programmed cell death in eukaryotic cells. In addition, mitochondria are also closely related to the innate immunity of host cells against viruses. The abnormality of mitochondrial morphology and function might lead to a variety of diseases. A large number of studies have found that a variety of viral infections could change mitochondrial dynamics, mediate mitochondria-induced cell death, and alter the mitochondrial metabolic status and cellular innate immune response to maintain intracellular survival. Meanwhile, mitochondria can also play an antiviral role during viral infection, thereby protecting the host. Therefore, mitochondria play an important role in the interaction between the host and the virus. Herein, we summarize how viral infections affect microbial pathogenesis by altering mitochondrial morphology and function and how viruses escape the host immune response.
Keywords: apoptosis; host innate immunity; mitochondrial fission and fusion; virus infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 201803020005/Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China
- 2019B020211003/the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong, China
- 202019071850100001/the Major Program of Guangdong Basic and Applied Research
- 2019KZDXM026/the Key Research Projects of Universities in Guangdong Province
- D20008/111 Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

