The Role of Galectin-9 as Mediator of Atopic Dermatitis: Effect on Keratinocytes
- PMID: 33923930
- PMCID: PMC8073283
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10040947
The Role of Galectin-9 as Mediator of Atopic Dermatitis: Effect on Keratinocytes
Abstract
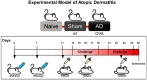
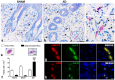
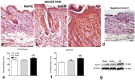
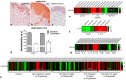
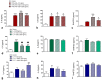
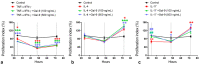
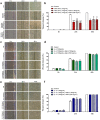
Galectin-9 (Gal-9) is a beta-galactoside-binding protein with a variety of biological functions related to immune response. However, in allergic diseases, its mechanism of action is not fully understood. This study evaluates the expression pattern of Gal-9 in patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), in ovalbumin (OVA)-induced experimental atopic dermatitis (AD) in mice, as well as its effect on human keratinocytes. The skin of OVA-immunized BALB/c mice was challenged with drops containing OVA on days 11, 14-18, and 21-24. HaCaT cells were cultured in the following experimental conditions: control (growth medium only) or stimulated with TNF-α/IFN-γ, or IL-4, or IL-17 with or without Gal-9 treatment. AD was characterized by increased levels of Gal-9 in mouse and human skin, especially in the epidermis, and with a marked influx of Gal-9 positive eosinophils and mast cells compared to the control group. Gal-9 showed an immunomodulatory effect on keratinocytes by decreasing the release of IL-6 by IL-4-stimulated keratinocytes or increasing the IL-6 and RANTES levels by IL-17- or TNF-α/IFN-γ-stimulated cells, respectively. Under IL-17, Gal-9 treatment also altered the proliferation rate of cells. Overall, increased levels of Gal-9 in AD skin contribute to the control of inflammatory response and the proliferative process of keratinocytes, suggesting this lectin as a relevant therapeutic target.
Keywords: IL-6; atopic dermatitis; eosinophil; galectin; keratinocyte; mast cell; skin inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

