Liquid Biopsy in Pancreatic Cancer: Are We Ready to Apply It in the Clinical Practice?
- PMID: 33924143
- PMCID: PMC8074327
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13081986
Liquid Biopsy in Pancreatic Cancer: Are We Ready to Apply It in the Clinical Practice?
Abstract
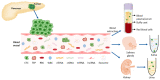
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) exhibits the poorest prognosis of all solid tumors, with a 5-year survival of less than 10%. To improve the prognosis, it is necessary to advance in the development of tools that help us in the early diagnosis, treatment selection, disease monitoring, evaluation of the response and prognosis. Liquid biopsy (LB), in its different modalities, represents a particularly interesting tool for these purposes, since it is a minimally invasive and risk-free procedure that can detect both the presence of genetic material from the tumor and circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in the blood and therefore distantly reflect the global status of the disease. In this work we review the current status of the main LB modalities (ctDNA, exosomes, CTCs and cfRNAs) for detecting and monitoring PDAC.
Keywords: CTCs; ctDNA; exosomes; liquid biopsy; miRNAs; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
N.R.-S. has received consulting and advisory honoraria from Amgen, Merck, Servier, Roche. J.F. has received consulting and advisory honoraria from Amgen, Ipsen, Eissai, Sirtex, Merck, Roche and Novartis; research funding from Merck, and travel and accommodation expenses from Amgen and Servier. V.H.-S. declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

