Host-Diet Effect on the Metabolism of Bifidobacterium
- PMID: 33924280
- PMCID: PMC8074910
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12040609
Host-Diet Effect on the Metabolism of Bifidobacterium
Abstract
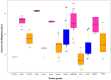
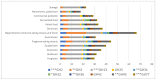
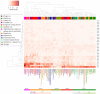
Bifidobacterium has a diverse host range and shows several beneficial properties to the hosts. Many species should have co-evolved with their hosts, but the phylogeny of Bifidobacterium is dissimilar to that of host animals. The discrepancy could be linked to the niche-specific evolution due to hosts' dietary carbohydrates. We investigated the relationship between bifidobacteria and their host diet using a comparative genomics approach. Since carbohydrates are the main class of nutrients for bifidobacterial growth, we examined the distribution of carbohydrate-active enzymes, in particular glycoside hydrolases (GHs) that metabolize unique oligosaccharides. When bifidobacterial species are classified by their distribution of GH genes, five groups arose according to their hosts' feeding behavior. The distribution of GH genes was only weakly associated with the phylogeny of the host animals or with genomic features such as genome size. Thus, the hosts' dietary pattern is the key determinant of the distribution and evolution of GH genes.
Keywords: Bifidobacterium; comparative genomics; evolution; glycoside hydrolase; phylogenetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Modesto M., Watanabe K., Arita M., Satti M., Oki K., Sciavilla P., Patavino C., Cammà C., Michelini S., Sgorbati B., et al. Bifidobacterium jacchi sp. nov., isolated from the faeces of a baby common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019;69:2477–2485. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.003518. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Modesto M., Satti M., Watanabe K., Puglisi E., Morelli L., Huang C.-H., Liou J.-S., Miyashita M., Tamura T., Saito S., et al. Characterization of Bifidobacterium species in feaces of the Egyptian fruit bat: Description of B. vespertilionis sp. nov. and B. rousetti sp. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2019;42:126017. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2019.126017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duranti S., Lugli G.A., Napoli S., Anzalone R., Milani C., Mancabelli L., Alessandri G., Turroni F., Ossiprandi M.C., Van Sinderen D., et al. Characterization of the phylogenetic diversity of five novel species belonging to the genus Bifidobacterium: Bifidobacterium castoris sp. nov., Bifidobacterium callimiconis sp. nov., Bifidobacterium goeldii sp. nov., Bifidobacterium samirii sp. nov. and Bifidobacterium dolichotidis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019;69:1288–1298. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.003306. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lugli G.A., Mangifesta M., Duranti S., Anzalone R., Milani C., Mancabelli L., Alessandri G., Turroni F., Ossiprandi M.C., van Sinderen D., et al. Phylogenetic classification of six novel species belonging to the genus Bifidobacterium comprising Bifidobacterium anseris sp. nov., Bifidobacterium criceti sp. nov., Bifidobacterium imperatoris sp. nov., Bifidobacterium italicum sp. nov., Bifidobacterium margollesii sp. nov. and Bifidobacterium parmae sp. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018;41:173–183. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2018.01.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

