Fully Bio-Based Thermosetting Polyurethanes from Bio-Based Polyols and Isocyanates
- PMID: 33924399
- PMCID: PMC8069015
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13081255
Fully Bio-Based Thermosetting Polyurethanes from Bio-Based Polyols and Isocyanates
Abstract
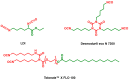
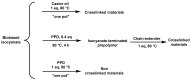
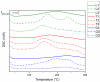
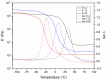
The trend towards the utilization of bioresources for the manufacturing of polymers has led industry players to bring to the market new monomers. In this work, we studied 3 polyisocyanates and 2 polyols with high renewable carbon contents, namely L-lysine ethyl ester diisocyanate (LDI), pentamethylene-diisocyanate (PDI) isocyanurate trimer, and hexamethylene-diisocyanate (HDI) allophanate as the isocyanates, as well as castor oil and polypropanediol as the polyols. These monomers are commercially available at a large scale and were used in direct formulations or used as prepolymers. Thermosetting polymers with Tg values ranging from -41 to +21 °C and thermal stabilities of up to 300 °C were obtained, and the polymerization was studied using NMR, DSC, and rheology. Cured materials were also characterized using FTIR, DMA, gel content, and swelling index determinations. These high bio-based content materials can successfully be obtained and could be used as alternatives to petro-based materials.
Keywords: allophanate; bio-based polymers; isocyanates; isocyanurate; lysine; polyols; polyurethanes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Skoczinski P., Chinthapalli R., Carus M., Baltus W., Guzman d.D., Käb H., Raschka A., Ravenstijn J. Bio-Based Building Blocks and Polymers-Global Capacities, Production and Trends 2019–2024. Nova-Institute; Hurth, Germany: 2019.
-
- Álvarez-Chávez C.R., Edwards S., Moure-Eraso R., Geiser K. Sustainability of bio-based plastics: General comparative analysis and recommendations for improvement. J. Clean. Prod. 2012;23:47–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.10.003. - DOI
-
- Caillol S., Boutevin B., Pascault J.-P. Handbook of Adhesive Technology. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2017. Bio-Sourced Epoxy Monomers and Polymers.
-
- Nikafshar S., Zabihi O., Hamidi S., Moradi Y., Barzegar S., Ahmadi M., Naebe M. A renewable bio-based epoxy resin with improved mechanical performance that can compete with DGEBA. RSC Adv. 2017;7:8694–8701. doi: 10.1039/C6RA27283E. - DOI
-
- Rad E.R., Vahabi H., de Anda A.R., Saeb M.R., Thomas S. Bio-epoxy resins with inherent flame retardancy. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019;135:608–612. doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.05.046. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

