Berberrubine Phosphate: A Selective Fluorescent Probe for Quadruplex DNA
- PMID: 33924894
- PMCID: PMC8124163
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26092566
Berberrubine Phosphate: A Selective Fluorescent Probe for Quadruplex DNA
Abstract
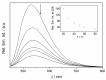
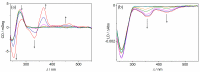
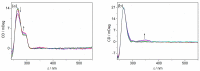
A phosphate-substituted, zwitterionic berberine derivative was synthesized and its binding properties with duplex DNA and G4-DNA were studied using photometric, fluorimetric and polarimetric titrations and thermal DNA denaturation experiments. The ligand binds with high affinity toward both DNA forms (Kb = 2-7 × 105 M-1) and induces a slight stabilization of G4-DNA toward thermally induced unfolding, mostly pronounced for the telomeric quadruplex 22AG. The ligand likely binds by aggregation and intercalation with ct DNA and by terminal stacking with G4-DNA. Thus, this compound represents one of the rare examples of phosphate-substituted DNA binders. In an aqueous solution, the title compound has a very weak fluorescence intensity (Φfl < 0.01) that increases significantly upon binding to G4-DNA (Φfl = 0.01). In contrast, the association with duplex DNA was not accompanied by such a strong fluorescence light-up effect (Φfl < 0.01). These different fluorimetric responses upon binding to particular DNA forms are proposed to be caused by the different binding modes and may be used for the selective fluorimetric detection of G4-DNA.
Keywords: DNA ligand; G4-DNA; alkaloids; light-up probe; quadruplex DNA; zwitterion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Yang X., Lovell J.F., Murthy N., Zhang Y. Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. Volume 34. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2020. pp. 33–53.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

