Tunable Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Coaxial Electrospun Composite Nanofibers of P(VDF-TrFE) and P(VDF-TrFE-CTFE)
- PMID: 33924977
- PMCID: PMC8124494
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094639
Tunable Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Coaxial Electrospun Composite Nanofibers of P(VDF-TrFE) and P(VDF-TrFE-CTFE)
Abstract
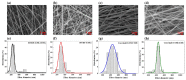
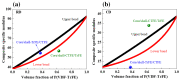
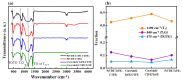
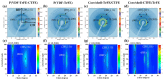
The coaxial core/shell composite electrospun nanofibers consisting of relaxor ferroelectric P(VDF-TrFE-CTFE) and ferroelectric P(VDF-TrFE) polymers are successfully tailored towards superior structural, mechanical, and electrical properties over the individual polymers. The core/shell-TrFE/CTFE membrane discloses a more prominent mechanical anisotropy between the revolving direction (RD) and cross direction (CD) associated with a higher tensile modulus of 26.9 MPa and good strength-ductility balance, beneficial from a better degree of nanofiber alignment, the increased density, and C-F bonding. The interfacial coupling between the terpolymer P(VDF-TrFE-CTFE) and copolymer P(VDF-TrFE) is responsible for comparable full-frequency dielectric responses between the core/shell-TrFE/CTFE and pristine terpolymer. Moreover, an impressive piezoelectric coefficient up to 50.5 pm/V is achieved in the core/shell-TrFE/CTFE composite structure. Our findings corroborate the promising approach of coaxial electrospinning in efficiently tuning mechanical and electrical performances of the electrospun core/shell composite nanofiber membranes-based electroactive polymers (EAPs) actuators as artificial muscle implants.
Keywords: coaxial electrospun core/shell nanofibers; dielectric constant; piezoelectricity; tensile modulus; wide-angle X-ray diffraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bar-Cohen Y., Anderson I.A. Electroactive polymer (EAP) actuators—Background review. Mech. Soft Mater. 2019;1:5. doi: 10.1007/s42558-019-0005-1. - DOI
-
- Zhang Z., Wang X., Tan S., Wang Q. Superior electrostrictive strain achieved under low electric fields in relaxor ferroelectric polymers. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2019;7:5201–5208. doi: 10.1039/C8TA11938D. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

