Rheological Behavior of a New Mucoadhesive Oral Formulation Based on Sodium Chondroitin Sulfate, Xyloglucan and Glycerol
- PMID: 33925057
- PMCID: PMC8167776
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb12020028
Rheological Behavior of a New Mucoadhesive Oral Formulation Based on Sodium Chondroitin Sulfate, Xyloglucan and Glycerol
Abstract
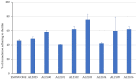
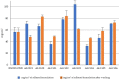
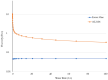
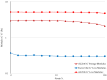
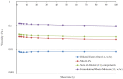
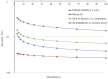
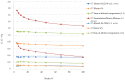
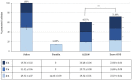
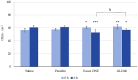
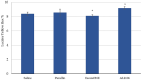
Background: The study aimed at assessing the mucoadhesive properties and the barrier effect of a formulation, labelled as AL2106, containing sodium chondroitin sulfate (ChS), xyloglucan from tamarind seed extract, and glycerol, by evaluating the capacity to adhere to a layer of mucin, the rheological synergism and the barrier effect in comparison to the marketed Esoxx One medical device. AL2106 is a medical device distributed by Alfasigma SpA, Italy with REF FTP57 (Manufacturer: Labomar SpA); it is analogous to Esoxx One medical device: the two products are drinkable solutions that, after swallowing, adhere to the esophageal mucosa, protecting it from the corrosive effect of the gastric acid reflux. AL2106 has been conceived to be better performing in terms of duration of the barrier effect compared to Esoxx One. Methods: The mucoadhesive properties, rheological behavior, buffering capacity against acidity, and film-forming ability with the resultant protecting effect on esophagus mucosa (caffeine permeation test) was compared between the two products. Results: The mucoadhesivity of the formulations was shown in vitro: both remained adherent to a mucin layer, also when the support was rotated by 90°, and when the film layer was washed with water, intended to simulate the washout due to swallowing. AL2106 showed a good buffering efficacy, being able to absorb at least 50% of its weight of 0.03 M HCl while maintaining the pH above 4. The film-forming effect and barrier properties of AL2106 and Esoxx One were confirmed by an in vitro study on reconstructed human esophageal epithelium. A greater film-forming efficacy of AL2106, lasting for at least 5 h, than Esoxx One was observed. Noteworthy, the barrier function of esophageal tissues was shown to be preserved after the application of both formulations. Conclusions: The combination of ChS with the mucoadhesive glycerol-xyloglucan complex and other excipients, which contribute to the barrier effect and to mucoadhesion, contained in AL2106, allowed a longer-lasting protective effect than Esoxx One, proving its effectivity and safety for oral use.
Keywords: GERD; epithelial barrier effect; film-forming capacity; mucoadhesion; rheology; viscosity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare to be the developers and actual suppliers of the studied formulations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effective Restoration of Gastric and Esophageal Tissues in an In Vitro Model of GERD: Mucoadhesive and Protective Properties of Xyloglucan, Pea Proteins, and Polyacrylic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 6;26(9):4409. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094409. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362645 Free PMC article.
-
Barrier Effect of a New Topical Agent on Damaged Esophageal Mucosa: Experimental Study on an ex vivo Swine Model.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2020 Nov 13;13:569-576. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S269568. eCollection 2020. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33223844 Free PMC article.
-
Barrier effect of Esoxx(®) on esophageal mucosal damage: experimental study on ex-vivo swine model.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2012;5:103-7. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S31404. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22767997 Free PMC article.
-
Xyloglucan, a Plant Polymer with Barrier Protective Properties over the Mucous Membranes: An Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 27;19(3):673. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030673. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29495535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rheological analysis and mucoadhesion: A 30 year-old and still active combination.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Jul 15;156:232-238. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.04.041. Epub 2018 Apr 25. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29729636 Review.
Cited by
-
The Design of Novel 3D-Printed, Moulded, and Oral Viscous Budesonide Formulations for Paediatrics: A Comparative Evaluation of Their Mucoadhesive Properties.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Oct 18;16(10):1338. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101338. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458665 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Study of the Method of Decorticating on Chemical Composition and Physicochemical Properties of Xyloglucan Extracted from Tamarindus indica L. Seeds at a Semi-Industrial Scale.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Feb 14;17(4):498. doi: 10.3390/polym17040498. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006160 Free PMC article.
-
Barrier effect and wound healing activity of the medical device REF-FTP78 in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 12;12(1):6136. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10171-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35414705 Free PMC article.
-
Effective Restoration of Gastric and Esophageal Tissues in an In Vitro Model of GERD: Mucoadhesive and Protective Properties of Xyloglucan, Pea Proteins, and Polyacrylic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 6;26(9):4409. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094409. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362645 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring a Novel Fasudil-Phospholipid Complex Formulated as Liposomal Thermosensitive in situ Gel for Glaucoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Jan 11;17:163-181. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S342975. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35046652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rubinstein A., Nakar D., Sintov A. Chondroitin sulfate: A potential biodegradable carrier for colon-specific drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 1992;84:141–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-5173(92)90054-6. - DOI
-
- Morreale P., Manopulo R., Galati M., Boccanera L., Saponati G., Bocchi L. Comparison of the antiinflammatory efficacy of chondroitin sulfate and diclofenac sodium in patients with knee osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1996;23:1385–1391. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

