Review of Microfluidic Methods for Cellular Lysis
- PMID: 33925101
- PMCID: PMC8145176
- DOI: 10.3390/mi12050498
Review of Microfluidic Methods for Cellular Lysis
Abstract
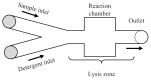
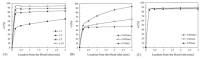
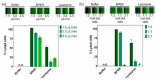
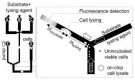
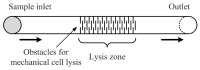
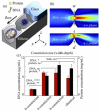
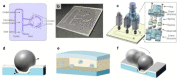
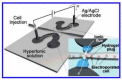
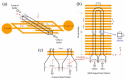
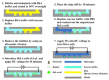
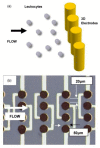
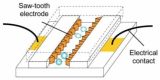
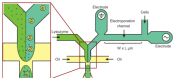
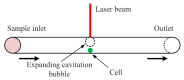
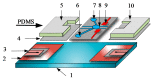
Cell lysis is a process in which the outer cell membrane is broken to release intracellular constituents in a way that important information about the DNA or RNA of an organism can be obtained. This article is a thorough review of reported methods for the achievement of effective cellular boundaries disintegration, together with their technological peculiarities and instrumental requirements. The different approaches are summarized in six categories: chemical, mechanical, electrical methods, thermal, laser, and other lysis methods. Based on the results derived from each of the investigated reports, we outline the advantages and disadvantages of those techniques. Although the choice of a suitable method is highly dependent on the particular requirements of the specific scientific problem, we conclude with a concise table where the benefits of every approach are compared, based on criteria such as cost, efficiency, and difficulty.
Keywords: cell lysis; cell membrane; microfluidics; review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


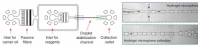








Similar articles
-
Performance Evaluation of Fast Microfluidic Thermal Lysis of Bacteria for Diagnostic Sample Preparation.Diagnostics (Basel). 2013 Jan 17;3(1):105-16. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics3010105. Diagnostics (Basel). 2013. PMID: 26835670 Free PMC article.
-
Low-voltage electrical cell lysis using a microfluidic device.Biomed Microdevices. 2019 Feb 21;21(1):22. doi: 10.1007/s10544-019-0369-x. Biomed Microdevices. 2019. PMID: 30790126
-
Lysis of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria by antibacterial porous polymeric monolith formed in microfluidic biochips for sample preparation.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014 Sep;406(24):5977-87. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-8028-9. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014. PMID: 25059724
-
Electrical lysis: dynamics revisited and advances in On-chip operation.Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2013;41(1):37-50. doi: 10.1615/critrevbiomedeng.2013006378. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2013. PMID: 23510008 Review.
-
Microfluidic sample preparation: cell lysis and nucleic acid purification.Integr Biol (Camb). 2009 Oct;1(10):574-86. doi: 10.1039/b905844c. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Integr Biol (Camb). 2009. PMID: 20023774 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced production of a recombinant xylanase (XT6): optimization of production and purification, and scaled-up batch fermentation in a stirred tank bioreactor.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 28;13(1):20895. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48202-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38017111 Free PMC article.
-
Flexible Liquid Crystal Polymer Technologies from Microwave to Terahertz Frequencies.Molecules. 2022 Feb 16;27(4):1336. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041336. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35209131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced microfluidic systems with temperature modulation for biological applications.Biomicrofluidics. 2025 May 1;19(3):031301. doi: 10.1063/5.0251893. eCollection 2025 May. Biomicrofluidics. 2025. PMID: 40322640 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient on-chip electrochemical lysing of foodborne bacteria for longer DNA strands with high yield for molecular analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 10;15(1):12305. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96886-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40211067 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the shear rate and residence time on the lysis of AC16 human cardiomyocyte cells via surface acoustic waves.Biomicrofluidics. 2023 Dec 6;17(6):064104. doi: 10.1063/5.0158977. eCollection 2023 Dec. Biomicrofluidics. 2023. PMID: 38074950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nguyen N., Wereley S. Fundamentals and Applications of Microfluidics. Artech House Publishing; Norwood, MA, USA: 2007.
-
- Islam M.S., Aryasomayajula T.A., Selvaganapathy P.R. A Review on Macroscale and Microscale Cell Lysis Methods. Micromachines. 2017;8:83. doi: 10.3390/mi8030083. - DOI
-
- Nandagopal M.S.G., Nakkeeran E., Prasanna V.R., Selvaraju N.N. Advance Microfluidic Approach over Conventional Batch and CTR for Improving the Efficiency of E-coli Cell Lysis by CuO Nanoparticles. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2016;15:20160105. doi: 10.1515/ijcre-2016-0105. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

