The Causes and Potential Injurious Effects of Elevated Serum Leptin Levels in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
- PMID: 33925217
- PMCID: PMC8125133
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094685
The Causes and Potential Injurious Effects of Elevated Serum Leptin Levels in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Abstract
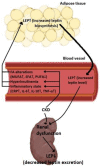
Leptin is an adipokine that regulates appetite and body mass and has many other pleiotropic functions, including regulating kidney function. Increased evidence shows that chronic kidney disease (CKD) is associated with hyperleptinemia, but the reasons for this phenomenon are not fully understood. In this review, we focused on potential causes of hyperleptinemia in patients with CKD and the effects of elevated serum leptin levels on patient kidney function and cardiovascular risk. The available data indicate that the increased concentration of leptin in the blood of CKD patients may result from both decreased leptin elimination from the circulation by the kidneys (due to renal dysfunction) and increased leptin production by the adipose tissue. The overproduction of leptin by the adipose tissue could result from: (a) hyperinsulinemia; (b) chronic inflammation; and (c) significant lipid disturbances in CKD patients. Elevated leptin in CKD patients may further deteriorate kidney function and lead to increased cardiovascular risk.
Keywords: adipose tissue; cardiovascular risk; chronic kidney disease; leptin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leptin as an uremic toxin: Deleterious role of leptin in chronic kidney disease.Biochimie. 2014 Oct;105:12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.06.024. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Biochimie. 2014. PMID: 25010649 Review.
-
Overview of the physiology and pathophysiology of leptin with special emphasis on its role in the kidney.Semin Nephrol. 2013 Jan;33(1):54-65. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.12.005. Semin Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23374894 Review.
-
Leptin Is Associated with Testosterone, Nutritional Markers, and Vascular Muscular Dysfunction in Chronic Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 12;25(14):7646. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147646. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062887 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin and leptin pathophysiology in chronic kidney disease.Pediatr Nephrol. 2013 Apr;28(4):611-6. doi: 10.1007/s00467-012-2380-9. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23229444 Review.
-
Obesity hypertension: the emerging role of leptin in renal and cardiovascular dyshomeostasis.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010 Jan;19(1):72-8. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e328332fb49. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010. PMID: 19851106 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic kidney disease combined with metabolic syndrome is a non-negligible risk factor.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Jul 25;15:20420188241252309. doi: 10.1177/20420188241252309. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39071115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From fat to filter: the effect of adipose tissue-derived signals on kidney function.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025 Jun;21(6):417-434. doi: 10.1038/s41581-025-00950-5. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40175570 Review.
-
Pediatric nephrotic syndrome: The interplay of oxidative stress and inflammation.J Med Biochem. 2024 Jun 15;43(4):424-435. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-46526. J Med Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39139165 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress on action and regulation of anorexigenic adipokine leptin.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 20;14:1172060. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1172060. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37547309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum leptin levels in patients with chronic kidney disease and hypertensive heart disease: An observational cross-sectional study.Health Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 19;6(1):e1053. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1053. eCollection 2023 Jan. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36698704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mota-Zamorano S., Luna E., Garcia-Pino G., González L.M., Gervasini G. Combined donor-recipient genotypes of leptin receptor and adiponectin gene polymorphisms affect the incidence of complications after renal transplantation. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2020;25:100648. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2020.100648. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Swierczynski J., Sledzinski T. Principles of Metabolic Surgery. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2012. The role of adipokines and gastrointestinal tract hormones in obesity; pp. 53–80.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

