Serum APOA4 Pharmacodynamically Represents Administered Recombinant Human Hepatocyte Growth Factor (E3112)
- PMID: 33925510
- PMCID: PMC8123842
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094578
Serum APOA4 Pharmacodynamically Represents Administered Recombinant Human Hepatocyte Growth Factor (E3112)
Abstract
Background: Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is an endogenously induced bioactive molecule that has strong anti-apoptotic and tissue repair activities. In this research, we identified APOA4 as a novel pharmacodynamic (PD) marker of the recombinant human HGF (rh-HGF), E3112.
Methods: rh-HGF was administered to mice, and their livers were investigated for the PD marker. Candidates were identified from soluble proteins and validated by using human hepatocytes in vitro and an animal disease model in vivo, in which its c-Met dependency was also ensured.
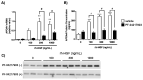
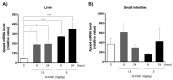
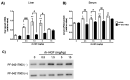
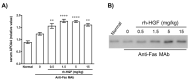
Results: Among the genes induced or highly enhanced after rh-HGF exposure in vivo, a soluble apolipoprotein, Apoa4, was found to be induced by rh-HGF in the murine liver. By using primary cultured human hepatocytes, the significant induction of human APOA4 was observed at the mRNA and protein levels, and it was inhibited in the presence of a c-Met inhibitor. Although mice constitutively expressed Apoa4 mRNA in the small intestine and the liver, the liver was the primary organ affected by administered rh-HGF to strongly induce APOA4 in a dose- and c-Met-dependent manner. Serum APOA4 levels were increased after rh-HGF administration, not only in normal mice but also in anti-Fas-induced murine acute liver failure (ALF), which confirmed the pharmacodynamic nature of APOA4.
Conclusions: APOA4 was identified as a soluble PD marker of rh-HGF with c-Met dependency. It should be worthwhile to clinically validate its utility through clinical trials with healthy subjects and ALF patients.
Keywords: ALF; APOA4; Fas; c-Met; rh-HGF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest associated with this research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Recombinant Human Hepatocyte Growth Factor on Hepatocytes Were Associated with Intrahepatic Hemorrhage Suppression Indicated by the Preservation of Prothrombin Time.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 12;20(8):1821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31013780 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and pharmacokinetics of recombinant human hepatocyte growth factor (rh-HGF) in patients with fulminant hepatitis: a phase I/II clinical trial, following preclinical studies to ensure safety.J Transl Med. 2011 May 8;9:55. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-55. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21548996 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antinecrotic and antiapoptotic effects of hepatocyte growth factor on cholestatic hepatitis in a mouse model of bile-obstructive diseases.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Feb;292(2):G639-46. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00292.2006. Epub 2006 Oct 26. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17068118
-
Hepatocyte growth factor twenty years on: Much more than a growth factor.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Jan;26 Suppl 1:188-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06549.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21199531 Review.
-
[Function and regulation of production of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2002 May;119(5):287-94, 309. doi: 10.1254/fpj.119.287. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2002. PMID: 12061140 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The distinct metabolism between large and small HDL indicates unique origins of human apolipoprotein A4.JCI Insight. 2023 Apr 24;8(8):e162481. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.162481. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 37092549 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding HDL Metabolism and Biology Through In Vivo Tracer Kinetics.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Jan;44(1):76-88. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.319742. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38031838 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gohda E., Tsubouchi H., Nakayama H., Hirono S., Sakiyama O., Takahashi K., Miyazaki H., Hashimoto S., Daikuhara Y. Purification and partial characterization of hepatocyte growth factor from plasma of a patient with fulminant hepatic failure. J. Clin. Investig. 1988;81:414–419. doi: 10.1172/JCI113334. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tsubouchi H., Hirono S., Gohda E., Nakayama H., Takahashi K., Sakiyama O., Miyazaki H., Sugihara J., Tomita E., Muto Y., et al. Clinical significance of human hepatocyte growth factor in blood from patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology. 1989;9:875–881. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090615. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Strain A.J., Ismail T., Tsubouchi H., Arakaki N., Hishida T., Kitamura N., Daikuhara Y., McMaster P. Native and recombinant human hepatocyte growth factors are highly potent promoters of DNA synthesis in both human and rat hepatocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1991;87:1853–1857. doi: 10.1172/JCI115207. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

