MicroRNA Expression in Extracellular Vesicles from Nasal Lavage Fluid in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
- PMID: 33925835
- PMCID: PMC8145239
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9050471
MicroRNA Expression in Extracellular Vesicles from Nasal Lavage Fluid in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Abstract
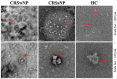
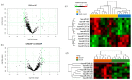
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanovesicles of endocytic origin released by cells and found in human bodily fluids. EVs contain both mRNA and microRNA (miRNA), which can be shuttled between cells, indicating their role in cell communication. This study investigated whether nasal secretions contain EVs and whether these EVs contain RNA. EVs were isolated from nasal lavage fluid (NLF) using sequential centrifugation. EVs were characterized and EV sizes were identified by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). In addition, EV miRNA expression was different in the chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyp (CRSsNP) and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp (CRSwNP) groups. The Kyoto encyclopedia gene and genome database (KEGG) database was used to identify pathways associated with changed miRNAs in each analysis group. Twelve miRNAs were differentially expressed in NLF-EVs of CRS patients versus HCs. In addition, eight miRNAs were differentially expressed in NLF-EVs of CRSwNP versus CRSsNP patients. The mucin-type O-glycan biosynthesis was a high-ranked predicted pathway in CRS patients versus healthy controls (HCs), and the Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway was a high-ranked predicted pathway in CRSwNP versus CRSsNP patients. We demonstrated the presence of and differences in NLF-EV miRNAs between CRS patients and HCs. These findings open up a broad and novel area of research on CRS pathophysiology as driven by miRNA cell communication.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; microRNAs; microarray analysis; nasal lavage fluid; sinusitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs regulating mucin type O-glycan biosynthesis and transforming growth factor β signaling pathways in nasal mucosa of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Northern China.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019 Jan;9(1):106-113. doi: 10.1002/alr.22230. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019. PMID: 30378273
-
MicroRNA expression profile of mature dendritic cell in chronic rhinosinusitis.Inflamm Res. 2015 Nov;64(11):885-93. doi: 10.1007/s00011-015-0870-5. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Inflamm Res. 2015. PMID: 26337346
-
Analysis of epidermal growth factor signaling in nasal mucosa epithelial cell proliferation involved in chronic rhinosinusitis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(19):3449-53. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014. PMID: 25269912
-
Harnessing microRNA-enriched extracellular vesicles for liquid biopsy.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Feb 21;11:1356780. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1356780. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38449696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research advances in roles of microRNAs in nasal polyp.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 25;13:1043888. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1043888. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36506304 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal Micro-RNAs as Intercellular Communicators in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 20;23(19):11047. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911047. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research progress of biomarkers in nasal secretions in endotypes diagnosis and clinical application of chronic rhinosinusitis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Nov;36(11):888-892. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.11.017. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36347587 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Insights into the epigenetics of chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps: a systematic review.Front Allergy. 2023 May 22;4:1165271. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2023.1165271. eCollection 2023. Front Allergy. 2023. PMID: 37284022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of exosomes for the alleviation of COVID-19-related pathologies.Cell Biochem Funct. 2022 Jul;40(5):430-438. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3720. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Cell Biochem Funct. 2022. PMID: 35647674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Exosomal microRNA Profiles Associated with Risk of Postoperative Recurrence in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Aug 23;17:5619-5631. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S472963. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39193125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xuan L., Luan G., Wang Y., Lan F., Zhang X., Hao Y., Zheng M., Wang X., Zhang L. MicroRNAs regulating mucin type O-glycan biosynthesis and transforming growth factor β signaling pathways in nasal mucosa of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Northern China. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019;9:106–113. doi: 10.1002/alr.22230. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

