Natural Products That Changed Society
- PMID: 33925870
- PMCID: PMC8146924
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9050472
Natural Products That Changed Society
Abstract
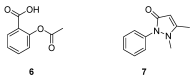
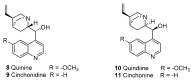
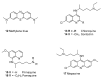
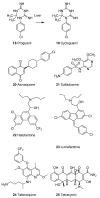
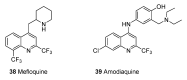
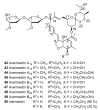
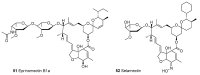
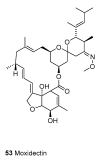
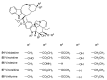
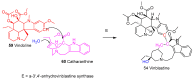
Until the end of the 19th century all drugs were natural products or minerals. During the 19th century chemists succeeded in isolating pure natural products such as quinine, morphine, codeine and other compounds with beneficial effects. Pure compounds enabled accurate dosing to achieve serum levels within the pharmacological window and reproducible clinical effects. During the 20th and the 21st century synthetic compounds became the major source of drugs. In spite of the impressive results achieved within the art of synthetic chemistry, natural products or modified natural products still constitute almost half of drugs used for treatment of cancer and diseases like malaria, onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis caused by parasites. A turning point in the fight against the devastating burden of malaria was obtained in the 17th century by the discovery that bark from trees belonging to the genus Cinchona could be used for treatment with varying success. However isolation and use of the active principle, quinine, in 1820, afforded a breakthrough in the treatment. In the 20th century the synthetic drug chloroquine severely reduced the burden of malaria. However, resistance made this drug obsolete. Subsequently artemisinin isolated from traditional Chinese medicine turned out to be an efficient antimalarial drug overcoming the problem of chloroquine resistance for a while. The use of synthetic analogues such as chloroquine or semisynthetic drugs such as artemether or artesunate further improved the possibilities for healing malaria. Onchocerciasis (river blindness) made life in large parts of Africa and South America miserable. The discovery of the healing effects of the macrocyclic lactone ivermectin enabled control and partly elimination of the disease by annual mass distribution of the drug. Also in the case of ivermectin improved semisynthetic derivatives have found their way into the clinic. Ivermectin also is an efficient drug for treatment of lymphatic filariasis. The serendipitous discovery of the ability of the spindle toxins to control the growth of fast proliferating cancer cells armed physicians with a new efficient tool for treatment of some cancer diseases. These possibilities have been elaborated through preparation of semisynthetic analogues. Today vincristine and vinblastine and semisynthetic analogues are powerful weapons against cancer diseases.
Keywords: artemisinin; cancer; chloroquine; ivermectin; malaria; moxidectin; onchocerciasis; quinine; vinblastine; vincristine.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
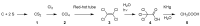



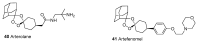

References
-
- Newman D.J., Cragg G.M. Natural Product Chemistry for Drug Discovery. Royal Society of Chemistry; London, UK: 2010. Natural products as drugs and leads to drugs: The historical perspective; pp. 3–27.
-
- Hyde K.D., Xu J., Rapior S., Jeewon R., Lumyong S., Niego A.G.A.T., Abeywickrama P.D., Aluthmuhandiram J.V.S., Brahamanage R.S., Brooks S., et al. The amazing potential of fungi: 50 ways we can exploit fungi industrially. Fungal Divers. 2019;97:1–136.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

