Protamine Sulfate Neutralization Profile of Various Dosages of Bovine, Ovine and Porcine UFHs and Their Depolymerized Derivatives in Non-Human Primates
- PMID: 33926250
- PMCID: PMC8114756
- DOI: 10.1177/10760296211005544
Protamine Sulfate Neutralization Profile of Various Dosages of Bovine, Ovine and Porcine UFHs and Their Depolymerized Derivatives in Non-Human Primates
Abstract
Introduction: Currently used unfractionated heparins (UFHs) and low molecular weight heparins (LMWHs) are derived from porcine intestinal mucosa. However, heparins have also been manufactured from tissues of other mammalian species such as cow (Bovine) and sheep (Ovine). Protamine sulphate (PS) is an effective inhibitor of heparin and is used clinically to neutralize both LMWH and UFH. In this study, we determined the PS neutralization profile of these agents in non-human primate model using anti-Xa and anti-IIa methods.
Material and methods: UFHs obtained from bovine, ovine and porcine mucosal tissues and their respective depolymerized LMWHs were administered at both, gravimetric (0.5 mg/kg) and potency adjusted (100 U/kg) dosages regimen intravenously to individual groups of primates in cross over studies. PS was administered at a fixed dosage and the relative neutralization of these anticoagulants was measured utilizing amidolytic anti-Xa and anti-IIa methods.
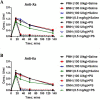
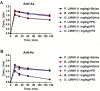
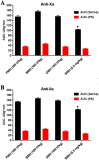
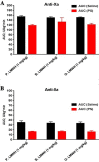
Results: These studies have demonstrated that, the equi-gravimetric dosages of BMH, PMH and OMH have comparable PS neutralization profiles. At potency adjusted dosages, all UFHs were completely neutralized by PS. Although comparable, the LMWHs were not fully neutralized by PS in both the anti-Xa and anti-IIa assays. PS was more efficient in neutralizing the anti-IIa effects of LMWHs.
Conclusion: Heparins of diverse origins showed comparable neutralization profiles by PS in the amidolytic anti-Xa and anti-IIa assays.
Keywords: LMWHs; UFHs; bovine; ovine; porcine; protamine sulfate.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Studies on Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor Antigen Release by Bovine, Ovine and Porcine Heparins Following Intravenous Administration to Non-Human Primates.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020 Jan-Dec;26:1076029620951851. doi: 10.1177/1076029620951851. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020. PMID: 33034200 Free PMC article.
-
Potency Adjusted Blended Heparin of Bovine, Ovine, and Porcine Heparin Exhibit Comparable Biologic Effects to Referenced Single-Sourced Porcine Heparin.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023 Jan-Dec;29:10760296231163251. doi: 10.1177/10760296231163251. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023. PMID: 36908199 Free PMC article.
-
Andexanet Alfa Neutralizes the Anticoagulant Effects of Unfractionated Heparin of Bovine, Ovine and Porcine Origin Almost as Protamine Sulfate.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2024 Jan-Dec;30:10760296241247558. doi: 10.1177/10760296241247558. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2024. PMID: 38656136 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and pharmacologic heterogeneity in low molecular weight heparins. Impact on the therapeutic profile.Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(9):983-99. doi: 10.2174/1381612043452811. Curr Pharm Des. 2004. PMID: 15078128 Review.
-
In vitro studies on the biochemistry and pharmacology of low molecular weight heparins.Semin Thromb Hemost. 1999;25 Suppl 3:27-33. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1999. PMID: 10549713 Review.
Cited by
-
What Do We Know about Peripartum Cardiomyopathy? Yesterday, Today, Tomorrow.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 30;25(19):10559. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910559. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Neutralization of Unfractionated Heparin and Enoxaparin by Andexanet Alfa.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2022 Jan-Dec;28:10760296221099934. doi: 10.1177/10760296221099934. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2022. PMID: 35535398 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wardrop D, Keeling D. The story of the discovery of heparin and warfarin. Br J Haematol. 2008;141(6):757–763. - PubMed
-
- Lehman CM, Frank EL. Laboratory monitoring of heparin therapy; partial thromboplastin time or anti-XA assay. Lab Med. 2009;40(1):47–51.
-
- Linhardt RJ, Gunay NS. Gunay, production and chemical processing of low molecular weight heparins. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1999;25(Suppl 3):5–16. - PubMed
-
- Johnston A, Hsieh SC, Carrier M. et al. A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines on the use of low molecular weight heparin and fondaparinux for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism: implications for research and policy decision-making. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0207410. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

