Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injection in Sports Injuries
- PMID: 33927829
- PMCID: PMC8046674
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-020-00349-3
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injection in Sports Injuries
Abstract
Background: Sports injuries are very common, and the management demands high degrees of skills and best techniques for an early return to play. The use of Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) injections in the treatment of tendon, muscle and ligament injuries has become popular. This study observes the outcomes of PRP injections in sports injuries.
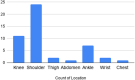
Methods: Forty-eight athletes (mean age 29.93 ± 8.48, Male: 37, Female: 11) presenting to a sports medicine centre with different sports injuries with symptom duration (2.81 ± 1.94) months were given PRP injections (single or multiple) four weeks apart with maximum number of injections up to three depending upon the clinical condition, Pre and Post VAS scores. Specific rehabilitation program was administered and compliance was graded by Sports Injury Rehabilitation Adherence Scale (SIRAS). A 1 year follow-up of cases was done for assessing player satisfaction and return to play.
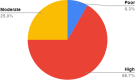
Results: Pre-procedure (7.25 ± 0.70) and post-procedure (2.42 ± 0.74) VAS score for all athletes showed significant difference with a p value at 0.0001. The average number of injections was 1.35 ± 1.41 with 72.91% requiring only one injection while 18.75% and 8.33% required two and three injections, respectively.
Conclusion: Athletes who required a single injection for acute injuries of lower grade returned to sports activity earlier than those who required multiple injections for chronic injuries. PRP injection has optimal effects on sports injuries not responding to conservative management.
Keywords: Patient satisfaction; Platelet-rich plasma; Rehabilitation; Return to sports; Sports injury; Ultrasound guided.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestOn behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Raeissadat, S. A., Sedighipour, L., Rayegani, S. M., Bahrami, M. H., Bayat, M., Rahimi, R. (2014). Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) versus Autologous Whole Blood on Pain and Function Improvement in Tennis Elbow: A Randomized Clinical Trial [Internet]. Vol. 2014, Pain Research and Treatment. Hindawi. p. e191525. Available from: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/prt/2014/191525/ Accessed 26 May 2020. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials