Modified laparoscopic toupet fundoplication with fundo-phrenico-pexy
- PMID: 33927870
- PMCID: PMC8068464
- DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjab136
Modified laparoscopic toupet fundoplication with fundo-phrenico-pexy
Abstract
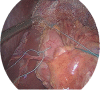
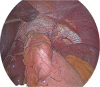
This article presents an alternative technique to the common Toupet fundoplication. It is a modern combination of the standard Toupet procedure and an additional fundophrenicopexie of the gastric wrap. In 1963 Toupet first described his technique of a fundoplication for reflux surgery. Over the past years this procedure has been modified and expanded many times. We have learned that the short gastric vessels need to be divided to get the wrap closer and easier around the esophagus. Furthermore, it is likely necessary to perform a balanced hiatoplasty to avoid slippage of the wrap. Our procedure is a modification of the standard Toupet fundoplication, but is extended by fixing the wrap to the anterior wall of the diaphragm. We consider our modification successful and safe in treating gastroesophageal reflux disease in patients with type I/II hiatal hernia and prevent postoperative complications such as dysphagia or slippage of the wrap.
Keywords: GERD; dysphagia; modified toupet fundoplication; reflux esophagitis; toupet fundoplication.
Published by Oxford University Press and JSCR Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2021.
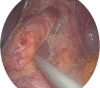
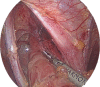
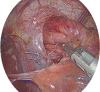
Figures
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

