Palm oil wastes as feedstock for lipase production by Yarrowia lipolytica and biocatalyst application/reuse
- PMID: 33927982
- PMCID: PMC7994466
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-021-02748-1
Palm oil wastes as feedstock for lipase production by Yarrowia lipolytica and biocatalyst application/reuse
Abstract
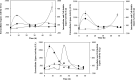
Palm oil production chain generates a greasy residue in the refining stage, the Palm Oil Deodorizer Distillate (PODD), mainly composed of free fatty acids. Palm oil is also used industrially to fry foods, generating a residual frying oil (RFO). In this paper, we aimed to produce lipase from palm agro-industrial wastes using an unconventional yeast. RFO_palm, from a known source, consisted of 0.11% MAG + FFA, 1.5% DAG, and 97.5 TAG, while RFO_commercial, from a commercial restaurant, contained 6.7% of DAG and 93.3% of TAG. All palm oil wastes were useful for extracellular lipase production, especially RFO_commercial that provided the highest activity (4.9 U/mL) and productivity (465 U/L.h) in 75 h of processing time. In 48 h of process, PODD presented 2.3 U/mL of lipase activity and 48.5 U/L.h of productivity. RFO_commercial also showed the highest values for lipase associated to cell debris (843 U/g). This naturally immobilized biocatalyst was tested on hydrolysis reactions to produce Lipolyzed Milk Fat and was quite efficient, with a hydrolysis yield of 13.1% and 3-cycle reuse. Therefore, oily palm residues seem a promising alternative to produce lipases by the non-pathogenic yeast Y. lipolytica and show great potential for industrial applications.
Keywords: Cell debris; Lipase; Natural immobilization; Palm oil deodorizer distillate; Residual frying oil; Waste valorization.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAll authors declare no competing/ conflicts of interests. The funders had no decision on the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Aguieiras ECG, De Barros DSN, Sousa H, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Freire DMG. Influence of the raw material on the final properties of biodiesel produced using lipase from Rhizomucor miehei grown on babassu cake as biocatalyst of esterification reactions. Renew Energy. 2017;113:112–118. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2017.05.090. - DOI
-
- Aguieiras ECG, Papadaki A, Mallouchos A, Mandala I, Sousa H, Freire DMG, Koutinas AA. Enzymatic synthesis of bio-based wax esters from palm and soybean fatty acids using crude lipases produced on agricultural residues. Ind Crops Prod. 2019;139:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111499. - DOI
-
- Ai O, Phuah E, Lee Y, Basiron Y. Palm oil. In: Shahidi F, editor. Bailey’s industrial oil and fat products. John Wiley and Sons; 2020.
-
- Akil E, Pereira AS, El-Bacha T, Amaral PFF, Torres AG. Efficient production of bioactive structured lipids by fast acidolysis catalyzed by Yarrowia lipolytica lipase, free and immobilized in chitosan-alginate beads, in solvent-free medium. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;163:910–918. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.282. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brígida AI, Amaral PFF, Gonçalves LR, Rocha-Leão MHM, Coelho MAZ. Yarrowia lipolytica IMUFRJ 50682: Lipase production in a multiphase bioreactor. Curr Biochem Eng. 2014;1:65–74. doi: 10.2174/22127119113019990005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

