DAND5 Inactivation Enhances Cardiac Differentiation in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- PMID: 33928078
- PMCID: PMC8078107
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.629430
DAND5 Inactivation Enhances Cardiac Differentiation in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
Abstract
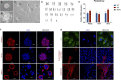
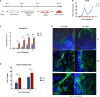
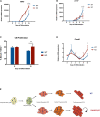
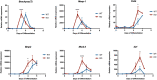
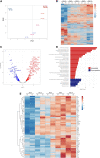
Deciphering the clues of a regenerative mechanism for the mammalian adult heart would save millions of lives in the near future. Heart failure due to cardiomyocyte loss is still one of the significant health burdens worldwide. Here, we show the potential of a single molecule, DAND5, in mouse pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes specification and proliferation. Dand5 loss-of-function generated the double of cardiac beating foci compared to the wild-type cells. The early formation of cardiac progenitor cells and the increased proliferative capacity of Dand5 KO mESC-derived cardiomyocytes contribute to the observed higher number of derived cardiac cells. Transcriptional profiling sequencing and quantitative RT-PCR assays showed an upregulation of early cardiac gene networks governing cardiomyocyte differentiation, cell cycling, and cardiac regenerative pathways but reduced levels of genes involved in cardiomyocyte maturation. These findings prompt DAND5 as a key driver for the generation and expansion of pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes systems with further clinical application purposes.
Keywords: Dand5; cardiac differentiation; cardiac progenitor cell; cardiomyocyte proliferation; embryonic stem cells.
Copyright © 2021 Inácio, von Gilsa Lopes, Silva, Cristo, Marques, Futschik and Belo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Belo J. A., Bachiller D., Agius E., Kemp C., Borges A. C., Marques S., et al. (2000). Cerberus-like is a secreted BMP and nodal antagonist not essential for mouse development. Genesis 26 265–270. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

