Mechanisms of action of ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified peptides (RiPPs)
- PMID: 33928382
- PMCID: PMC8183687
- DOI: 10.1093/jimb/kuab005
Mechanisms of action of ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified peptides (RiPPs)
Abstract
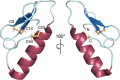
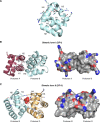
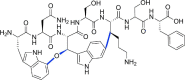
Natural products remain a critical source of medicines and drug leads. One of the most rapidly growing superclasses of natural products is RiPPs: ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified peptides. RiPPs have rich and diverse bioactivities. This review highlights examples of the molecular mechanisms of action that underly those bioactivities. Particular emphasis is placed on RiPP/target interactions for which there is structural information. This detailed mechanism of action work is critical toward the development of RiPPs as therapeutics and can also be used to prioritize hits in RiPP genome mining studies.
Keywords: Mechanism of action; Natural products; RiPPs.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology.
Figures
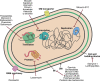
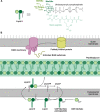
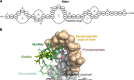
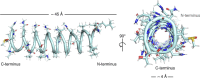
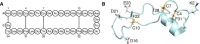



References
-
- Allgaier H., Jung G., Werner R. G., Schneider U., Zähner H. (1985). Elucidation of the structure of epidermin, a ribosomally synthesized, tetracyclic heterodetic polypeptide antibiotic. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 24, 1051–1053. 10.1002/anie.198510511. - DOI
-
- Anderssen E. L., Diep D. B., Nes I. F., Eijsink V. G. H., Nissen-Meyer J. (1998). Antagonistic activity of Lactobacillus plantarum C11: Two new two- peptide bacteriocins, plantaricins EF and JK, and the induction factor plantaricin A. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64, 2269–2272. 10.1128/aem.64.6.2269-2272.1998. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

