Effect of hemopexin treatment on outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice
- PMID: 33930375
- PMCID: PMC8206022
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147507
Effect of hemopexin treatment on outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice
Abstract
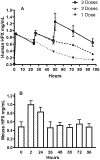
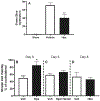
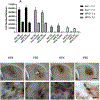
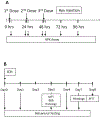
Heme release from hemoglobin may contribute to secondary injury after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). The primary endogenous defense against heme toxicity is hemopexin, a 57 kDa glycoprotein that is depleted in the CNS after hemorrhagic stroke. We hypothesized that systemic administration of exogenous hemopexin would reduce perihematomal injury and improve outcome after experimental ICH. Intraperitoneal treatment with purified human plasma hemopexin beginning 2 h after striatal ICH induction and repeated daily for the following two days reduced blood-brain barrier disruption and cell death at 3 days. However, it had no effect on neurological deficits at 4 or 7 days or striatal cell viability at 8 days. Continuous daily hemopexin administration had no effect on striatal heme content at 3 or 7 days, and did not attenuate neurological deficits, inflammatory cell infiltration, or perihematomal cell viability at 8 days. These results suggest that systemic hemopexin treatment reduces early injury after ICH, but this effect is not sustained, perhaps due to an imbalance between striatal tissue heme and hemopexin content at later time points. Future studies should investigate its effect when administered by methods that more efficiently target CNS delivery.
Keywords: Heme; Hemoglobin toxicity; Iron; Stroke; Stroke models; Subararachnoid hemorrhage.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest: None
Figures


References
-
- Bakker WW, Borghuis T, Harmsen MC, van den Berg A, Kema IP, Niezen KE, Kapojos JJ, 2005. Protease activity of plasma hemopexin. Kidney International. 68, 603–10. - PubMed
-
- Bakker WW, Melgert BN, Faas MM, 2010. Hemopexin: anti-inflammatory, pro-inflammatory, or both? Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 87, 1–2; author reply 3, 5. - PubMed
-
- Belcher JD, Chen C, Nguyen J, Abdulla F, Zhang P, Nguyen H, Nguyen P, Killeen T, Miescher SM, Brinkman N, Nath KA, Steer CJ, Vercellotti GM, 2018. Haptoglobin and hemopexin inhibit vaso-occlusion and inflammation in murine sickle cell disease: Role of heme oxygenase-1 induction. PLoS One. 13, e0196455. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

