Evaluation of deep learning approaches for identification of different corona-virus species and time series prediction
- PMID: 33930734
- PMCID: PMC8062905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2021.101921
Evaluation of deep learning approaches for identification of different corona-virus species and time series prediction
Abstract
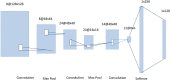
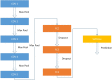
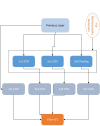
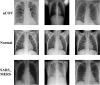
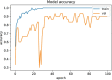
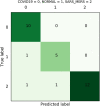
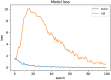
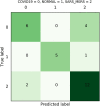
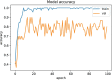
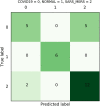
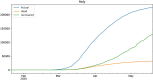
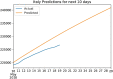
Novel corona-virus (nCOV) has been declared as a pandemic that started from the city Wuhan of China. This deadly virus is infecting people rapidly and has targeted 4.93 million people across the world, with 227 K people being infected only in Italy. Cases of nCOV are quickly increasing whereas the number of nCOV test kits available in hospitals are limited. Under these conditions, an automated system for the classification of patients into nCOV positive and negative cases, is a much needed tool against the pandemic, helping in a selective use of the limited number of test kits. In this research, Convolutional Neural Network-based models (one block VGG, two block VGG, three block VGG, four block VGG, LetNet-5, AlexNet, and Resnet-50) have been employed for the detection of Corona-virus and SARS_MERS infected patients, distinguishing them from the healthy subjects, using lung X-ray scans, which has proven to be a challenging task, due to overlapping characteristics of different corona virus types. Furthermore, LSTM model has been used for time series forecasting of nCOV cases, in the following 10 days, in Italy. The evaluation results obtained, proved that the VGG1 model distinguishes the three classes at an accuracy of almost 91%, as compared to other models, whereas the approach based on the LSTM predicts the number of nCOV cases with 99% accuracy.
Keywords: Convolutional Neural Networks; LSTM; NCOV; VGG-16.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection and analysis of nucleic acid in various biological samples of COVID-19 patients.Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020 Sep-Oct;37:101673. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101673. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32311437 Free PMC article.
-
Novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV: prevalence, biological and clinical characteristics comparison with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Feb;24(4):2012-2019. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202002_20379. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32141570
-
Potential Maternal and Infant Outcomes from (Wuhan) Coronavirus 2019-nCoV Infecting Pregnant Women: Lessons from SARS, MERS, and Other Human Coronavirus Infections.Viruses. 2020 Feb 10;12(2):194. doi: 10.3390/v12020194. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32050635 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Dynamics and Clinical Features of Novel Corona Virus (2019-nCoV).Altern Ther Health Med. 2020 Aug;26(S2):50-53. Altern Ther Health Med. 2020. PMID: 32710732 Review.
-
Mysterious Virus: A Review on Behavior and Treatment Approaches of the Novel Coronavirus, 2019-nCoV.Arch Med Res. 2020 Jul;51(5):375-383. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.04.022. Epub 2020 May 6. Arch Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32448490 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An efficient hardware architecture based on an ensemble of deep learning models for COVID -19 prediction.Sustain Cities Soc. 2022 May;80:103713. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2022.103713. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Sustain Cities Soc. 2022. PMID: 35136715 Free PMC article.
-
The Applications of Nanopore Sequencing Technology in Animal and Human Virus Research.Viruses. 2024 May 16;16(5):798. doi: 10.3390/v16050798. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38793679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection and Prevention of Virus Infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1368:21-52. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-8969-7_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35594019
-
Deep learning based hybrid prediction model for predicting the spread of COVID-19 in the world's most populous countries.Expert Syst Appl. 2023 Nov 30;231:120769. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120769. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Expert Syst Appl. 2023. PMID: 37334273 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Medical Diagnosis: A Novel Two-Phase Deep Learning Framework for Adversarial Proof Disease Detection in Radiology Images.J Imaging Inform Med. 2024 Feb;37(1):308-338. doi: 10.1007/s10278-023-00916-8. Epub 2024 Jan 10. J Imaging Inform Med. 2024. PMID: 38343214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basu S., Mitra S. 2020. Deep Learning for Screening Covid-19 Using Chest X-ray Images.arXiv:2004.10507 (arXiv preprint)
-
- Bio, https://biodifferences.com/difference-between-x-ray-and-ct-scan.html (May 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

