Distinct circadian mechanisms govern cardiac rhythms and susceptibility to arrhythmia
- PMID: 33931651
- PMCID: PMC8087694
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22788-8
Distinct circadian mechanisms govern cardiac rhythms and susceptibility to arrhythmia
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Distinct circadian mechanisms govern cardiac rhythms and susceptibility to arrhythmia.Nat Commun. 2021 Dec 8;12(1):7284. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27498-9. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34880252 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Electrical activity in the heart exhibits 24-hour rhythmicity, and potentially fatal arrhythmias are more likely to occur at specific times of day. Here, we demonstrate that circadian clocks within the brain and heart set daily rhythms in sinoatrial (SA) and atrioventricular (AV) node activity, and impose a time-of-day dependent susceptibility to ventricular arrhythmia. Critically, the balance of circadian inputs from the autonomic nervous system and cardiomyocyte clock to the SA and AV nodes differ, and this renders the cardiac conduction system sensitive to decoupling during abrupt shifts in behavioural routine and sleep-wake timing. Our findings reveal a functional segregation of circadian control across the heart's conduction system and inherent susceptibility to arrhythmia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



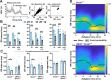
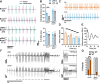

References
-
- Guo YF, Stein PK. Circadian rhythm in the cardiovascular system: chronocardiology. Am. Heart J. 2003;145:779–786. - PubMed
-
- Martino TA, Young ME. Influence of the cardiomyocyte circadian clock on cardiac physiology and pathophysiology. J. Biol. Rhythms. 2015;30:183–205. - PubMed
-
- Scheer FAJL, Horst Ter, Van Der Vliet GJ, Buijs J. Physiological and anatomic evidence for regulation of the heart by suprachiasmatic nucleus in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Hear. Circ. Physiol. 2001;280:1391–1399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PG/19/82/34760/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- BB/I019405/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J017744/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R21 CA227381/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- BB/I018654/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

