Development of a high-sensitivity ELISA detecting IgG, IgA and IgM antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein in serum and saliva
- PMID: 33932228
- PMCID: PMC8242512
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.13349
Development of a high-sensitivity ELISA detecting IgG, IgA and IgM antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein in serum and saliva
Abstract
Detecting antibody responses during and after SARS-CoV-2 infection is essential in determining the seroepidemiology of the virus and the potential role of antibody in disease. Scalable, sensitive and specific serological assays are essential to this process. The detection of antibody in hospitalized patients with severe disease has proven relatively straightforward; detecting responses in subjects with mild disease and asymptomatic infections has proven less reliable. We hypothesized that the suboptimal sensitivity of antibody assays and the compartmentalization of the antibody response may contribute to this effect. We systematically developed an ELISA, optimizing different antigens and amplification steps, in serum and saliva from non-hospitalized SARS-CoV-2-infected subjects. Using trimeric spike glycoprotein, rather than nucleocapsid, enabled detection of responses in individuals with low antibody responses. IgG1 and IgG3 predominate to both antigens, but more anti-spike IgG1 than IgG3 was detectable. All antigens were effective for detecting responses in hospitalized patients. Anti-spike IgG, IgA and IgM antibody responses were readily detectable in saliva from a minority of RT-PCR confirmed, non-hospitalized symptomatic individuals, and these were mostly subjects who had the highest levels of anti-spike serum antibodies. Therefore, detecting antibody responses in both saliva and serum can contribute to determining virus exposure and understanding immune responses after SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; ELISA; SARS-CoV-2; antibodies.
© 2021 The Authors. Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
AC and SH are employed by the Binding Site Group Ltd. AH has a commercial relationship with Binding Site Group Ltd. MTD and MG have a commercial relationship with Abingdon Health. The rest of the authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
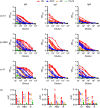
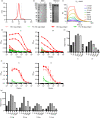
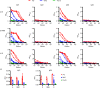
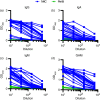
Update of
-
Detection of antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein in both serum and saliva enhances detection of infection.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jun 18:2020.06.16.20133025. doi: 10.1101/2020.06.16.20133025. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: Immunology. 2021 Sep;164(1):135-147. doi: 10.1111/imm.13349. PMID: 32588002 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- WHO . Coronavirus disease (COVID‐19) Situation Report ‐ 141. 2020.
-
- Woo PC, Lau SK, Wong BH, Chan KH, Hui WT, Kwan GS, et al. False‐positive results in a recombinant severe acute respiratory syndrome‐associated coronavirus (SARS‐CoV) nucleocapsid enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay due to HCoV‐OC43 and HCoV‐229E rectified by Western blotting with recombinant SARS‐CoV spike polypeptide. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:5885–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wibroe PP, Helvig SY, Moein MS. The role of complement in antibody therapy for infectious diseases. Microbiol Spectr. 2014;2:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

