Conformational flexibility and structural variability of SARS-CoV2 S protein
- PMID: 33932324
- PMCID: PMC8086150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2021.04.006
Conformational flexibility and structural variability of SARS-CoV2 S protein
Abstract
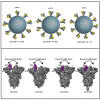
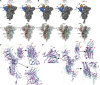
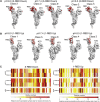
Spike (S) glycoprotein of SARS-CoV2 exists chiefly in two conformations, open and closed. Most previous structural studies on S protein have been conducted at pH 8.0, but knowledge of the conformational propensities under both physiological and endosomal pH conditions is important to inform vaccine development. Our current study employed single-particle cryoelectron microscopy to visualize multiple states of open and closed conformations of S protein at physiological pH 7.4 and near-physiological pH 6.5 and pH 8.0. Propensities of open and closed conformations were found to differ with pH changes, whereby around 68% of S protein exists in open conformation at pH 7.4. Furthermore, we noticed a continuous movement in the N-terminal domain, receptor-binding domain (RBD), S2 domain, and stalk domain of S protein conformations at various pH values. Several key residues involving RBD-neutralizing epitopes are differentially exposed in each conformation. This study will assist in developing novel therapeutic measures against SARS-CoV2.
Keywords: 3D reconstruction; S-head; TEM; cryo-EM; negative staining; pH-dependent; single particle; solvent accessibility; spike homotrimer; stalk domain.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Batishchev O.V., Shilova L.A., Kachala M.V., Tashkin V.Y., Sokolov V.S., Fedorova N.V., Baratova L.A., Knyazev D.G., Zimmerberg J., Chizmadzhev Y.A. pH-dependent formation and disintegration of the influenza A virus protein scaffold to provide tension for membrane fusion. J. Virol. 2016;90:575–585. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

