Molecular mechanisms and treatments for ocular symblephara
- PMID: 33932469
- PMCID: PMC8553799
- DOI: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2021.04.008
Molecular mechanisms and treatments for ocular symblephara
Abstract
There are currently no effective methods to prevent or durably treat ocular symblephara, the adhesions between the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva. How symblephara form at the molecular level is largely unknown. We present here an overview of current clinical symblephara treatments and describe potential molecular mechanisms behind conjunctival adhesion formation that may inform future symblephara treatment and prevention options. Understanding how symblephara form at the molecular level will facilitate treatment development. Preventative therapies may be possible by targeting symblephara progenitor cells immediately after injuries, while novel therapeutics should be aimed at modulating TGF-β pathways and effector cells in conjunctival scarring to treat symblephara formation more effectively.
Keywords: Conjunctival inflammation; Molecular mechanisms; Preventative therapies; Symblephara; Treatments.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

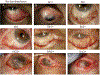
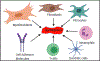

References
-
- Agha E El, Kramann R, Schneider RK, Li X, Seeger W, Humphreys BD, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Fibrotic Disease. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21(2):166–77. - PubMed
-
- Andreev K, Zenkel M, Kruse F, Jünemann A, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U. Expression of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), their receptors, and activins in normal and scarred conjunctiva: Role of BMP-6 and activin-A in conjunctival scarring? Exp Eye Res. 2006;83(5):1162–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

