Effect of omega-3 fatty acids supplementation on cardio-metabolic and oxidative stress parameters in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33933009
- PMCID: PMC8088683
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-021-02351-9
Effect of omega-3 fatty acids supplementation on cardio-metabolic and oxidative stress parameters in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Omega-3 fatty acids (FAs) have been suggested as a beneficial supplement in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients, but the results of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) are controversial. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate all the RCTs about the impact of omega-3 FAs supplementation on cardiometabolic outcomes and oxidative stress parameters in patients with CKD.
Methods: We performed a systematic database search in PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBASE, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane Central, up to May 2020. We included all placebo-controlled randomized trials that assessed the effect of omega-3 FAs supplementation on any cardiometabolic outcomes: blood pressure, total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or triglycerides (TG) and oxidative stress parameters. Data were pooled using DerSimonian-Laird's random-effects model.
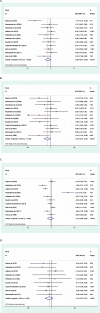
Results: Finally, thirteen articles met the inclusion criteria for this review omega-3 FAs supplementation significantly decrease TC (SMD: -0.26; 95% CI: - 0.51, - 0.02; I2 = 52.7%), TG (SMD: -0.22; 95% CI: - 0.43, - 0.02; I2 = 36.0%) and Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels (SMD: -0.91; 95% CI: - 1.29, - 0.54; I2 = 00.0%) and also significantly increase superoxide dismutase (SOD) (SMD: 0.58; 95% CI: 0.27, 0.90; I2 = 00.0%) and Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) (SMD: 0.50; 95% CI: 0.14, 0.86; I2 = 00.0%) activities. However our results show that omega-3 FAs supplementation have no significant effects on HDL, LDL and blood pressure. Conclusion This systematic review and meta-analysis supports current evidence for the clinical benefit of omega-3 FAs intake to improve cardiometabolic parameters in CKD patients. However, well-designed RCTs still needed to provide a conclusive picture in this field.
Keywords: Blood lipids; CKD; Cardio-metabolic outcomes; Omega-3 FAs; Oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Khandouzi N, Shidfar F, Agah S, Hosseini AF, Dehnad A. Comparison of the effects of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on the eradication of helicobacter pylori infection, serum inflammatory factors and total antioxidant capacity. Iranian journal of pharmaceutical research: IJPR. 2015;14(1):149–157. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

