In silico screening of potent bioactive compounds from honeybee products against COVID-19 target enzymes
- PMID: 33934306
- PMCID: PMC8088405
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-14195-9
In silico screening of potent bioactive compounds from honeybee products against COVID-19 target enzymes
Abstract
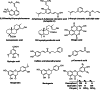
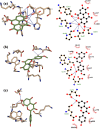
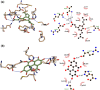
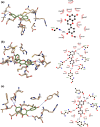
After the early advent of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, myriads of FDA-approved drugs have been massively repurposed for COVID-19 treatment based on molecular docking against selected protein targets that play fundamental roles in the replication cycle of the novel coronavirus. Honeybee products are well known of their nutritional values and medicinal effects. Bee products contain bioactive compounds in the form of a collection of phenolic acids, flavonoids, and terpenes of natural origin that display wide spectrum antiviral effects. We revealed by molecular docking the profound binding affinity of 14 selected phenolics and terpenes present in honey and propolis (bees glue) against the main protease (Mpro) and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) enzymes of the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus (the causative agent of COVID-19) using AutoDock Vina software. Of these compounds, p-coumaric acid, ellagic acid, kaempferol, and quercetin have the strongest interaction with the SARS-CoV-2 target enzymes, and it may be considered an effective COVID-19 inhibitor.
Keywords: COVID-19; Drug repurposing; Honeybee products; Molecular docking; Natural products; Phenolic compounds.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Raltegravir, Indinavir, Tipranavir, Dolutegravir, and Etravirine against main protease and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2: A molecular docking and drug repurposing approach.J Infect Public Health. 2020 Dec;13(12):1856-1861. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.10.015. Epub 2020 Oct 26. J Infect Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33168456 Free PMC article.
-
Putative SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitors from an In-House Library of Natural and Nature-Inspired Products: A Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking Study.Molecules. 2020 Aug 17;25(16):3745. doi: 10.3390/molecules25163745. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32824454 Free PMC article.
-
Propolis, Bee Honey, and Their Components Protect against Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review of In Silico, In Vitro, and Clinical Studies.Molecules. 2021 Feb 25;26(5):1232. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051232. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33669054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico prediction of potential inhibitors for the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 using molecular docking and dynamics simulation based drug-repurposing.J Infect Public Health. 2020 Sep;13(9):1210-1223. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.016. Epub 2020 Jun 16. J Infect Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32561274 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Candidates against COVID-19 Targeting RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022;23(3):396-419. doi: 10.2174/1389201022666210421102513. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 33882805 Review.
Cited by
-
The Breadth of Bacteriophages Contributing to the Development of the Phage-Based Vaccines for COVID-19: An Ideal Platform to Design the Multiplex Vaccine.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 12;24(2):1536. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021536. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Alkaloids from Marine-Derived Fungi as Drug Leads versus COVID-19 Infection: A Computational Approach to Explore their Anti-COVID-19 Activity and ADMET Properties.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 8;2022:5403757. doi: 10.1155/2022/5403757. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35911157 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Viral and Immunomodulatory Properties of Propolis: Chemical Diversity, Pharmacological Properties, Preclinical and Clinical Applications, and In Silico Potential against SARS-CoV-2.Foods. 2021 Jul 31;10(8):1776. doi: 10.3390/foods10081776. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34441553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Updates on Naturally Occurring Compounds Recognizing SARS-CoV-2 Druggable Targets.Molecules. 2021 Jan 26;26(3):632. doi: 10.3390/molecules26030632. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33530467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin and luteolin are single-digit micromolar inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 22;12(1):10571. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14664-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35732785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Naggar, Yahya, Sun J, Robertson A, Giesy JP, Wiseman S (2016) Chemical characterization and antioxidant properties of Canadian propolis. In J Apic Res 55(4):305–314.10.1080/00218839.2016.1233700
-
- Al Naggar Y, Yahya G, Al-Kahtani S, Stangaciu S, El-Seedi H (2021) Back to Ancient Remedy: Could Inhalation of Aerosolised-Honey and Propolis Tincture Protect Against the COVID-19 Pandemic? J Apither 8(2):1–5
-
- Bafna K, Krug RM, Montelione GT (2020) Structural similarity of SARS-CoV2 Mpro and HCV NS3/4A proteases suggests new approaches for identifying existing drugs useful as COVID-19 therapeutics. In ChemRxiv. 10.26434/chemrxiv.12153615
-
- Biopharma products in development for COVID-19 (2021). Available online at https://www.bioworld.com/COVID19products, updated on 1/14/2021, checked on 1/14/2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

