From Womb to Neighborhood: A Racial Analysis of Social Determinants of Psychosis in the United States
- PMID: 33934608
- PMCID: PMC8655820
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20071091
From Womb to Neighborhood: A Racial Analysis of Social Determinants of Psychosis in the United States
Abstract
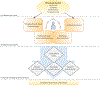
The authors examine U.S.-based evidence that connects characteristics of the social environment with outcomes across the psychosis continuum, from psychotic experiences to schizophrenia. The notion that inequitable social and economic systems of society significantly influence psychosis risk through proxies, such as racial minority and immigrant statuses, has been studied more extensively in European countries. While there are existing international reviews of social determinants of psychosis, none to the authors' knowledge focus on factors in the U.S. context specifically-an omission that leaves domestic treatment development and prevention efforts incomplete and underinformed. In this review, the authors first describe how a legacy of structural racism in the United States has shaped the social gradient, highlighting consequential racial inequities in environmental conditions. The authors offer a hypothesized model linking structural racism with psychosis risk through interwoven intermediary factors based on existing theoretical models and a review of the literature. Neighborhood factors, cumulative trauma and stress, and prenatal and perinatal complications were three key areas selected for review because they reflect social and environmental conditions that may affect psychosis risk through a common pathway shaped by structural racism. The authors describe evidence showing that Black and Latino people in the United States suffer disproportionately from risk factors within these three key areas, in large part as a result of racial discrimination and social disadvantage. This broad focus on individual and community factors is intended to provide a consolidated space to review this growing body of research and to guide continued inquiries into social determinants of psychosis in U.S. contexts.
Keywords: Environmental Risk Factors; Racism; Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorders; Sociopolitical Issues.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Niendam is a founder and shareholder in Safari Health, Inc. The other authors report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Structural Racism as a Proximal Cause for Race-Related Differences in Psychiatric Disorders.Am J Psychiatry. 2021 Jul;178(7):579-581. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2021.21050486. Am J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34270341 No abstract available.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Social Determinants of Health, 2018. https://health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/social-determinants...
-
- Allen J, Balfour R, Bell R, et al.: Social determinants of mental health. Int Rev Psychiatry 2014; 26:392–407 - PubMed
-
- Silva M, Loureiro A, Cardoso G: Social determinants of mental health: a review of the evidence. Eur J Psychiatry 2016; 30:259–292
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical