Interventional nephrology and vascular access practice: A perspective from South and Southeast Asia
- PMID: 33934667
- PMCID: PMC7615897
- DOI: 10.1177/11297298211011375
Interventional nephrology and vascular access practice: A perspective from South and Southeast Asia
Abstract
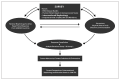
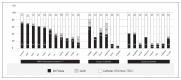
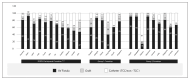
South and Southeast Asia is the most populated, heterogeneous part of the world. The Association of Vascular Access and InTerventionAl Renal physicians (AVATAR Foundation), India, gathered trends on epidemiology and Interventional Nephrology (IN) for this region. The countries were divided as upper-middle- and higher-income countries as Group-1 and lower and lower-middle-income countries as Group-2. Forty-three percent and 70% patients in the Group 1 and 2 countries had unplanned hemodialysis (HD) initiation. Among the incident HD patients, the dominant Vascular Access (VA) was non-tunneled central catheter (non-TCC) in 70% of Group 2 and tunneled central catheter (TCC) in 32.5% in Group 1 countries. Arterio-Venous Fistula (AVF) in the incident HD patients was observed in 24.5% and 35% of patients in Group-2 and Group-1, respectively. Eight percent and 68.7% of the prevalent HD patients in Group-2 and Group-1 received HD through an AVF respectively. Nephrologists performing any IN procedure were 90% and 60% in Group-2 and Group 1, respectively. The common procedures performed by nephrologists include renal biopsy (93.3%), peritoneal dialysis (PD) catheter insertion (80%), TCC (66.7%) and non-TCC (100%). Constraints for IN include lack of time (73.3%), lack of back-up (40%), lack of training (73.3%), economic issues (33.3%), medico-legal problems (46.6%), no incentive (20%), other interests (46.6%) and institution not supportive (26%). Routine VA surveillance is performed in 12.5% and 83.3% of Group-2 and Group-1, respectively. To conclude, non-TCC and TCC are the most common vascular access in incident HD patients in Group-2 and Group-1, respectively. Lack of training, back-up support and economic constraints were main constraints for IN growth in Group-2 countries.
Keywords: AV fistula; Southeast Asia; Vascular access; interventional nephrology (IN); tunneled catheter; vascular access surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
Interventional nephrology in Australia and New Zealand.J Vasc Access. 2023 Nov;24(6):1538-1539. doi: 10.1177/11297298221077776. Epub 2022 Feb 9. J Vasc Access. 2023. PMID: 35139676 No abstract available.
References
-
- Southern Asia Population (LIVE) https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/southern-asia-population/
-
- South-Eastern Asia Population (LIVE) https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/south-eastern-asia-popula...
-
- What Are The Five Regions of Asia? https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/the-four-regions-of-asia.html .
-
- Human Development Indices and Indicators. 2018 Statistical Update, Published for the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) http://hdr.undp.org/en/content/human-development-indices-indicators-2018... .
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical