Economic and Humanistic Burden Associated with Depression and Anxiety Among Adults with Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases (NCCDs) in the United States
- PMID: 33935498
- PMCID: PMC8079356
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S280200
Economic and Humanistic Burden Associated with Depression and Anxiety Among Adults with Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases (NCCDs) in the United States
Abstract
Introduction: Patients with both major depressive disorder (MDD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in addition to one or multiple comorbid non-communicable chronic diseases (NCCDs) face unique challenges. However, few studies have characterized how the burden of co-occurring MDD and GAD differs from that of only MDD or only GAD among patients with NCCDs.
Methods: In this study, we used Medical Expenditures Panel Survey data from 2010-2017 to understand how the economic and humanistic burden of co-occurring MDD and GAD differs from that of MDD or GAD alone among patients with NCCDs. We used generalized linear models to investigate this relationship and controlled for patient sociodemographics and clinical characteristics.
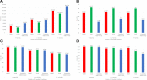
Results: Co-occurring MDD and GAD was associated with increases in mean annual per patient inpatient visits, office visits, emergency department visits, annual drug costs, and total medical costs. Among patients with 3+ NCCDs, MDD or GAD only was associated with lower odds ratios (ORs) of limitations in activities of daily living (ADLs; 0.532 and 0.508, respectively) and social (0.503, 0.526) and physical limitations (0.613, 0.613) compared to co-occurring MDD and GAD. Compared to patients with co-occurring MDD and GAD, having MDD only or GAD only was associated with significantly lower odds of cognitive limitations (0.659 and 0.461, respectively) in patients with 1-2 NCCDs and patients with 3+ NCCDs (0.511, 0.416).
Discussion: Comorbid MDD and GAD was associated with higher economic burden, lower quality of life, and greater limitations in daily living compared to MDD or GAD alone. Health-related economic and humanistic burden increased with number of NCCDs.
Keywords: anxiety; depression; economic burden; humanistic burden; non-communicable diseases.
© 2021 Armbrecht et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Eric Armbrecht reports personal fees from Pfizer and grants from the State of Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services during the conduct of the study as well as grants from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, outside the submitted work. Ruchit Shah, Gregory Poorman, and Jennifer M Stephens are employees of Pharmerit International, which received financial support from Pfizer in connection with this study; Linlin Luo was an employee of Pharmerit International when the study was conducted. Benjamin Li is an employee of Pfizer and owns Pfizer stock. Elizabeth Pappadopulos and Seema Haider were employees of Pfizer when the study was conducted (legacy Upjohn, a division of Pfizer, now part of Viatris Inc.). Dr Roger S McIntyre reports grants from CIHR/GACD/Chinese National Natural Research Foundation; and personal fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Allergan, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Minerva, Intra-Cellular, Abbvie, and Eisai. Dr. Roger S McIntyre is a shareholder in The 420 Company and CEO of Champignon. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

