Nasal Sprays Containing Mometasone Furoate for Relief of Post-Adenotonsillectomy Pain in Children: A Prospective Controlled Study
- PMID: 33935543
- PMCID: PMC8085455
- DOI: 10.14744/SEMB.2020.75735
Nasal Sprays Containing Mometasone Furoate for Relief of Post-Adenotonsillectomy Pain in Children: A Prospective Controlled Study
Abstract
Objectives: Adenotonsillectomy is one of most common surgeries performed in childhood. Post-operative pain associated particularly with tonsillectomy is still a problem for many physicians. Despite advances in surgical techniques, analgesics, or anti-inflammatory drugs, no unique strategy for post-tonsillectomy pain management has been suggested. The aim of this study is to investigate the analgesic effect of steroid containing nasal spray applied to tonsillar region after tonsillectomy.
Methods: Eighty-two patients were assigned into two groups as study and control. In study group, nasal spray containing steroid was applied to each tonsillar region after surgery for 5 days. Post-operative pain of all patients was assessed using a visual analog scale and results were compared.
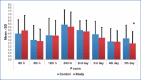
Results: Pain decreased gradually over time in both the study and control groups. Although the pain scores from 4 h post-surgery to post-operative day 5 were not found to significantly decrease in children that used nasal spray containing steroid, these patients developed less pain on post-operative day 5,with statistical significance (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Post-tonsillectomy pain was reported to increase around post-operative day 5, which coincides with the time of intense wound inflammation. Therefore, significant pain reduction on post-operative day 5 observed in children that used nasal spray with steroid may have clinical importance for overcoming this problem.
Keywords: Mometasone furoate; nasal spray; pain relief; steroid; tonsillectomy; visual analogue scale.
Copyright: © 2021 by The Medical Bulletin of Sisli Etfal Hospital.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Shapiro N. Tonsillectomy myths. AAO-HNS Bulletin. 2005;24:12–3.
-
- Randall DA, Hoffer ME. Complications of tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998;118:61–8. - PubMed
-
- Duval M, Wilkes J, Korgenski K, Srivastava R, Meier J. Causes costs, and risk factors for unplanned return visits after adenotonsillectomy in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;79:1640–6. - PubMed
-
- Curtis JL, Harvey DB, Willie S, Narasimhan E, Andrews S, Henrichsen J, et al. Causes and costs for ED visits after pediatric adenotonsillectomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;152:691–6. - PubMed
-
- Anderson BJ, Ralph CJ, Stewart AW, Barber C, Holford NH. The dose-effect relationship for morphine and vomiting after day-stay tonsillectomy in children. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2000;28:155–60. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
