Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Experimental Ischemic Stroke: A Preclinical Systematic Review
- PMID: 33935650
- PMCID: PMC8079818
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2021.628908
Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Experimental Ischemic Stroke: A Preclinical Systematic Review
Abstract
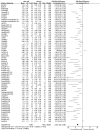
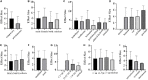
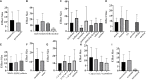
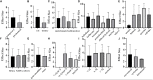
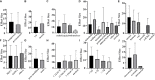
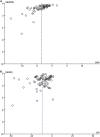
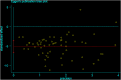
Stem cell transplantation offers promise in the treatment of ischemic stroke. Here we utilized systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression to study the biological effect of stem cell treatments in animal models of ischemic stroke. A total of 98 eligible publications were included by searching PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science from inception to August 1, 2020. There are about 141 comparisons, involving 5,200 animals, that examined the effect of stem cell transplantation on neurological function and infarct volume as primary outcome measures in animal models for stroke. Stem cell-based therapy can improve both neurological function (effect size, -3.37; 95% confidence interval, -3.83 to -2.90) and infarct volume (effect size, -11.37; 95% confidence interval, -12.89 to -9.85) compared with controls. These results suggest that stem cell therapy could improve neurological function deficits and infarct volume, exerting potential neuroprotective effect for experimental ischemic stroke, but further clinical studies are still needed.
Keywords: ischemic stroke; middle cerebral artery occlusion; neuroprotection; pre-clinical systematic review; stem cell-based therapy.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Zhang, Huang, Zheng, Ying, Zhang, Lu, Wang and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Meta-Analysis of the Safety and Efficacy of Stem Cell Therapies for Ischemic Stroke in Preclinical and Clinical Studies.Stem Cells Dev. 2019 Apr 15;28(8):497-514. doi: 10.1089/scd.2018.0218. Stem Cells Dev. 2019. PMID: 30739594
-
Therapeutic potential of stem cell extracellular vesicles for ischemic stroke in preclinical rodent models: a meta-analysis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Apr 3;14(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03270-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37013588 Free PMC article.
-
Role of histone deacetylases and sirtuins in the ischaemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies.Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2025 May 7:svn-2025-004159. doi: 10.1136/svn-2025-004159. Online ahead of print. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40341167
-
Resveratrol has an Overall Neuroprotective Role in Ischemic Stroke: A Meta-Analysis in Rodents.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 20;12:795409. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.795409. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34987407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraparenchymal Neural Stem/Progenitor Cell Transplantation for Ischemic Stroke Animals: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Oct 2;2018:4826407. doi: 10.1155/2018/4826407. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 30369951 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A review and meta-analysis of stem cell therapies in stroke patients: effectiveness and safety evaluation.Neurol Sci. 2024 Jan;45(1):65-74. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-07032-z. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 37733251 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of the efficacy of intra-arterial and intravenous transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived neural progenitor cells in experimental stroke.PeerJ. 2023 Nov 9;11:e16358. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16358. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38025691 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicle-Derived miRNAs in Ischemic Stroke: Roles in Neuroprotection, Tissue Regeneration, and Biomarker Potential.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Mar 31;45(1):31. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01551-3. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40164816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MCC950 Regulates Stem Cells Destiny Through Modulating SIRT3-NLRP3 Inflammasome Dynamics During Oxygen Glucose Deprivation.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Jul;19(5):1415-1426. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10520-6. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 36811746
-
Targeting Neurogenesis in Seeking Novel Treatments for Ischemic Stroke.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 13;11(10):2773. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102773. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893146 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andrews E. M., Tsai S. Y., Johnson S. C., Farrer J. R., Wagner J. P., Kopen G. C., et al. (2008). Human adult bone marrow-derived somatic cell therapy results in functional recovery and axonal plasticity following stroke in the rat. Exp. Neurol. 211 588–592. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.02.027 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

