AHL-Lactonase Producing Psychrobacter sp. From Palk Bay Sediment Mitigates Quorum Sensing-Mediated Virulence Production in Gram Negative Bacterial Pathogens
- PMID: 33935995
- PMCID: PMC8079732
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.634593
AHL-Lactonase Producing Psychrobacter sp. From Palk Bay Sediment Mitigates Quorum Sensing-Mediated Virulence Production in Gram Negative Bacterial Pathogens
Abstract
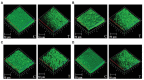
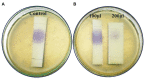
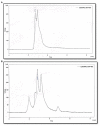
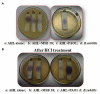
Quorum sensing (QS) is a signaling mechanism governed by bacteria used to converse at inter- and intra-species levels through small self-produced chemicals called N-acylhomoserine lactones (AHLs). Through QS, bacteria regulate and organize the virulence factors' production, including biofilm formation. AHLs can be degraded by an action called quorum quenching (QQ) and hence QQ strategy can effectively be employed to combat biofilm-associated bacterial pathogenesis. The present study aimed to identify novel bacterial species with QQ potential. Screening of Palk Bay marine sediment bacteria for QQ activity ended up with the identification of marine bacterial isolate 28 (MSB-28), which exhibited a profound QQ activity against QS biomarker strain Chromobacterium violaceum ATCC 12472. The isolate MSB-28 was identified as Psychrobacter sp. through 16S-rRNA sequencing. Psychrobacter sp. also demonstrated a pronounced activity in controlling the biofilm formation in different bacteria and biofilm-associated virulence factors' production in P. aeruginosa PAO1. Solvent extraction, heat inactivation, and proteinase K treatment assays clearly evidence the enzymatic nature of the bioactive lead. Furthermore, AHL's lactone ring cleavage was confirmed with experiments including ring closure assay and chromatographic analysis, and thus the AHL-lactonase enzyme production in Psychrobacter sp. To conclude, this is the first report stating the AHL-lactonase mediated QQ activity from marine sediment bacteria Psychrobacter sp. Future work deals with the characterization, purification, and mass cultivation of the purified protein and should pave the way to assessing the feasibility of the identified protein in controlling QS and biofilm-mediated multidrug resistant bacterial infections in mono or multi-species conditions.
Keywords: AHL-lactonase; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Psychrobacter sp.; marine Palk Bay sediment; quorum quenching.
Copyright © 2021 Packiavathy, Kannappan, Thiyagarajan, Srinivasan, Jeyapragash, Paul, Velmurugan and Ravi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Babu T. G., Nithyanand P., Babu N. K. C., Pandian S. K. (2009). Evaluation of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide as a potential short-term preservative agent for stripped goat skin. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25, 901–907. 10.1007/s11274-009-9969-6 - DOI
-
- Carlier A., Uroz S., Smadja B., Fray R., Latour X., Dessaux Y., et al. (2003). The Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens harbors an attM-paralogous gene, aiiB, also encoding N-acyl homoserine lactone lactonase activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 4989–4993. 10.1128/aem.69.8.4989-4993.2003, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

