The Mechanism of Action of Antigen Processing Independent T Cell Epitopes Designed for Immunotherapy of Autoimmune Diseases
- PMID: 33936079
- PMCID: PMC8079784
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.654201
The Mechanism of Action of Antigen Processing Independent T Cell Epitopes Designed for Immunotherapy of Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
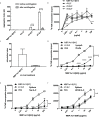
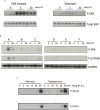
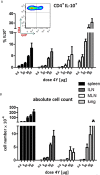
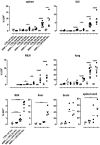
Immunotherapy with antigen-processing independent T cell epitopes (apitopes) targeting autoreactive CD4+ T cells has translated to the clinic and been shown to modulate progression of both Graves' disease and multiple sclerosis. The model apitope (Ac1-9[4Y]) renders antigen-specific T cells anergic while repeated administration induces both Tr1 and Foxp3+ regulatory cells. Here we address why CD4+ T cell epitopes should be designed as apitopes to induce tolerance and define the antigen presenting cells that they target in vivo. Furthermore, we reveal the impact of treatment with apitopes on CD4+ T cell signaling, the generation of IL-10-secreting regulatory cells and the systemic migration of these cells. Taken together these findings reveal how apitopes induce tolerance and thereby mediate antigen-specific immunotherapy of autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: Tr1 cell; apitope; autoimmune disease; dendritic cell; immunological tolerance; immunotherapy; interleukin-10; synthetic peptide.
Copyright © 2021 Shepard, Wegner, Hill, Burton, Aerts, Schurgers, Hoedemaekers, Ng, Streeter, Jansson and Wraith.
Conflict of interest statement
DW is Professor of Immunology at the University of Birmingham and CSO and Founder of Apitope International NV; ES, BH and LJ are or were recent employees of Apitope International NV. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wraith DC. Designing antigens for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases. Curr Opin Chem Eng (2018) 19:35–42. 10.1016/j.coche.2017.12.004 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

