Novel Biomarkers of Dynamic Blood PD-L1 Expression for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients
- PMID: 33936103
- PMCID: PMC8085403
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.665133
Novel Biomarkers of Dynamic Blood PD-L1 Expression for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have become a high-profile regimen for malignancy recently. However, only a small subpopulation obtains long-term clinical benefit. How to select optimal patients by reasonable biomarkers remains a hot topic.
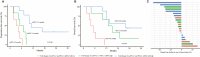
Methods: Paired tissue samples and blood samples from 51 patients with advanced malignancies were collected for correlation analysis. Dynamic changes in blood PD-L1 (bPD-L1) expression, including PD-L1 mRNA, exosomal PD-L1 (exoPD-L1) protein and soluble PD-L1 (sPD-L1), were detected after 2 months of ICIs treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. The best cutoff values for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of all three biomarkers were calculated with R software.
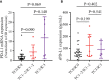
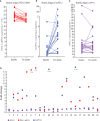
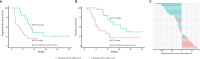
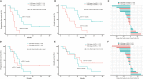
Results: In 51 cases of various malignancies, those with positive tissue PD-L1 (tPD-L1) had significantly higher PD-L1 mRNA than those with negative tPD-L1. In 40 advanced NSCLC patients, those with a fold change of PD-L1 mRNA ≥ 2.04 had better PFS, OS and best objective response (bOR) rate. In addition, a fold change of exoPD-L1 ≥ 1.86 was also found to be associated with better efficacy and OS in a cohort of 21 advanced NSCLC cases. The dynamic change of sPD-L1 was not associated with efficacy and OS. Furthermore, the combination of PD-L1 mRNA and exoPD-L1 could screen better patients for potential benefit from ICIs treatment.
Conclusion: There was a positive correlation between bPD-L1 and tPD-L1 expression. Increased expression of PD-L1 mRNA, exoPD-L1, or both in early stage of ICIs treatment could serve as positive biomarkers of efficacy and OS in advanced NSCLC patients.
Keywords: NSCLC; biomarker; blood PD-L1; exosome; immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Copyright © 2021 Yang, Chen, Gu, Niu, Zhao, Zheng, Xu, Yu, Li, Meng, Chen, Zhuo, Zhang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, et al. Five-Year Survival and Correlates Among Patients With Advanced Melanoma, Renal Cell Carcinoma, or Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Nivolumab. JAMA Oncol (2019) 5(10):1411–20. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2187 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

