Hydrogen bond design principles
- PMID: 33936251
- PMCID: PMC8087110
- DOI: 10.1002/wcms.1477
Hydrogen bond design principles
Abstract
Hydrogen bonding principles are at the core of supramolecular design. This overview features a discussion relating molecular structure to hydrogen bond strengths, highlighting the following electronic effects on hydrogen bonding: electronegativity, steric effects, electrostatic effects, π-conjugation, and network cooperativity. Historical developments, along with experimental and computational efforts, leading up to the birth of the hydrogen bond concept, the discovery of nonclassical hydrogen bonds (C-H…O, O-H…π, dihydrogen bonding), and the proposal of hydrogen bond design principles (e.g., secondary electrostatic interactions, resonance-assisted hydrogen bonding, and aromaticity effects) are outlined. Applications of hydrogen bond design principles are presented.
Keywords: aromaticity; hydrogen bonding; resonance-assisted hydrogen bonding; secondary electrostatic interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures

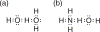










References
-
- Latimer WM, Rodebush WH. Polarity and ionization from the standpoint of the Lewis theory of valence. J Am Chem Soc. 1920;42(7): 1419–1433.
-
- Jeffrey GA. An introduction to hydrogen bonding. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997.
-
- Lewis GN. Valence and the structure of atoms and molecules. New York, NY: Chemical Catalog Co., 1923. p. 109.
-
- Watson JD, Crick FHC. Molecular structure of nucleic acids: A structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature. 1953;171:737–738. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
