A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Risk Factors Associated with Severity and Death in COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 33936349
- PMCID: PMC8040926
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6660930
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Risk Factors Associated with Severity and Death in COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
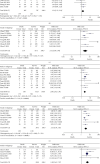
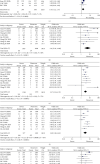
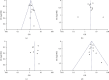
This meta-analysis aims to screen the risk factors for severe illness and death and provide help for early clinical treatment of the new coronavirus (COVID-19). Based on a comprehensive search of PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science databases, we included studies that explored the cause and risk factors for severe illness and death in COVID-19 patients. We evaluated the strength of this relationship using odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). A total of 17 articles were included; 16 of the 17 articles were from China, and the risk factors associated with severe illness and death were age, sex, and multiple comorbidities. Advanced age (≥65 years, severe illness, OR = 2.62; death, OR = 6.00), male (severe illness, OR = 1.49; death, OR = 1.54), chronic respiratory diseases (severe illness, OR = 5.67; death, OR = 3.72), diabetes (severe illness, OR = 3.27; death, OR = 2.60), hypertension (severe illness, OR = 3.08; death, OR = 3.53), chronic kidney disease (severe illness, OR = 3.59; death, OR = 5.38), and cardiovascular diseases (severe illness, OR = 3.87; death, OR = 4.91) were all risk factors. For COVID-19 patients, advanced age, male, and patients with chronic disease are at higher risk of developing severe illness or even death.
Copyright © 2021 Pengqiang Du et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest associated with the publication of this manuscript.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

