Reduced circulating exosomal miR-382 predicts unfavorable outcome in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 33936369
- PMCID: PMC8085833
Reduced circulating exosomal miR-382 predicts unfavorable outcome in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
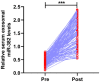
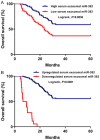
Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) have been demonstrated as robust and promising biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Our aim was to determine the significance of serum exosomal miR-382 in NSCLC. Circulating exosomes were collected from 126 patients with NSCLC and 60 normal controls before treatment and one month after surgery. The circulating exosomal miR-382 expression was measured with quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) in all the participants. Our findings demonstrated that circulating exosomal miR-382 was very reduced in NSCLC. In addition, it showed high accuracy for discriminating NSCLC patients from healthy subjects. Interestingly, serum exosomal miR-382 improved the diagnostic accuracy of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). Moreover, its level increased significantly one month following surgical resection. Reduced circulating exosomal miR-382 was positively associated with poor clinical variables. NSCLC cases with lower serum exosomal miR-382 suffered worse overall survival (OS) and serum exosomal miR-382 was independently associated with OS. Taken together, circulating exosomal miR-382 is a robust biomarker for evaluating the progression of NSCLC.
Keywords: Circulating exosomal miR-382; NSCLC; prognosis.
IJCEP Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Serum exosomal miR-378 upregulation is associated with poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jun;34(6):e23237. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23237. Epub 2020 Feb 14. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32061007 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of serum exosomal miR-216b predicts unfavorable prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Biomark. 2020;27(1):113-120. doi: 10.3233/CBM-190914. Cancer Biomark. 2020. PMID: 31771047
-
Early diagnostic and prognostic value of serum exosomal miR-1246 in non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020 Jul 1;13(7):1601-1607. eCollection 2020. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32782678 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating exosomal microRNA-4497 as a potential biomarker for metastasis and prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023 Aug;248(16):1403-1413. doi: 10.1177/15353702231184223. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023. PMID: 37551102 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating exosomal microRNAs as prognostic biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):13048-13058. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14369. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28055956 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exosomal miR-338-3p suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer cells metastasis by inhibiting CHL1 through the MAPK signaling pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 30;12(11):1030. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04314-2. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34718336 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Prognostic Significance of Exosomes and Their Components in Patients With Cancers.Cancer Med. 2025 Jan;14(1):e70569. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70569. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 39757782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liquid biopsy: Exosomal microRNAs as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2022 Feb 16;21(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01525-9. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35172817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional tumor-derived exosomes in NSCLC progression and clinical implications.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 19;16:1485661. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1485661. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40176898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging functions and clinical applications of exosomal microRNAs in diseases.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 May 9;8(3):350-362. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.05.004. eCollection 2023 Sep. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 37250456 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schwartz AG, Cote ML. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;893:21–41. - PubMed
-
- Zheng M. Classification and pathology of lung cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016;25:447–468. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez de Cos J, Sojo Gonzalez MA, Montero MV, Perez Calvo MC, Vicente MJ, Valle MH. Non-small cell lung cancer and silent brain metastasis. Survival and prognostic factors. Lung Cancer. 2009;63:140–145. - PubMed
-
- Bahce I, Yaqub M, Smit EF, Lammertsma AA, van Dongen GA, Hendrikse NH. Personalizing NSCLC therapy by characterizing tumors using TKI-PET and immuno-PET. Lung Cancer. 2017;107:1–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
